Benzophenone is an organic compound widely used in industry for its photoprotective and stabilizing properties. Found in cosmetics , inks, and packaging , it plays a key role in preserving products exposed to ultraviolet light. However, its use is the subject of debate due to its potential effects on human health and the environment. Classified as an endocrine disruptor and probable carcinogen, benzophenone is subject to strict regulations aimed at limiting its use. This article explores its chemical characteristics, benzophenone dosage , applications, and the risks associated with its use.
In this context, laboratory analyses are essential to guarantee product conformity, and companies like YesWeLab support manufacturers in their control and compliance processes.
1. What is benzophenone (CAS: 119-61-9)?
Definition and chemical structure
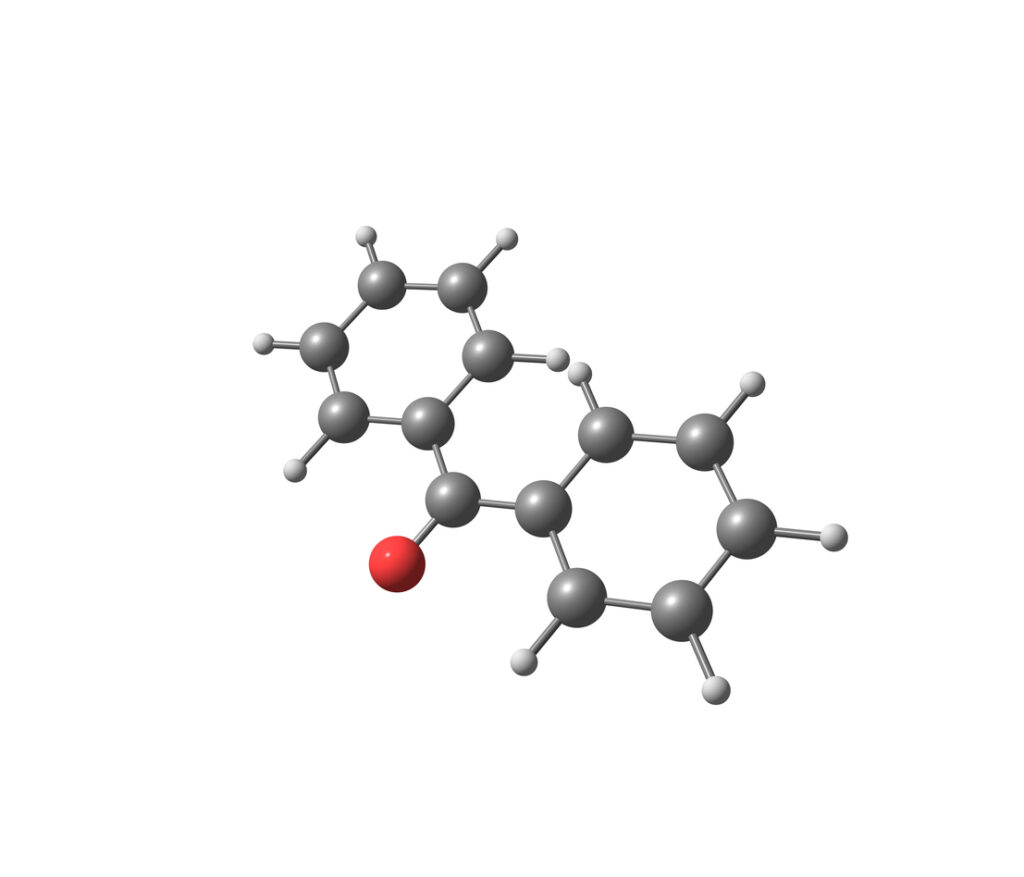
Benzophenone is a molecule belonging to the aromatic ketone family. It consists of a diphenylmethane ring to which a carbonyl group (C=O) is attached. Its molecular formula is C₁₃H₁₀O , which gives it a rigid and stable structure.
This compound is classified as a bicyclic , meaning it contains two benzene rings linked by a central carbon atom. This chemical characteristic gives it a high capacity for absorbing ultraviolet rays, explaining its use as a UV filter in many industrial products.
Structurally, benzophenone is a nonpolar molecule, making it soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, or toluene. However, it is practically insoluble in water , which can promote its accumulation in biological and environmental environments.
Physical and chemical properties
Benzophenone possesses several physicochemical properties that influence its industrial use:
- Molar mass : 182.22 g/mol
- Melting point : 48-49°C
- Boiling point : 305°C
- Solubility : Soluble in organic solvents, very slightly soluble in water
- Density : 1.114 g/cm³
- Vapor pressure : Low, which limits its evaporation at room temperature
Thanks to its thermal and chemical stability, benzophenone is resistant to degradation under the effect of light and heat, making it an ideal additive to protect various materials against premature aging.
Industrial synthesis of benzophenone
Benzophenone can be synthesized by several industrial methods. One of the most common involves the oxidation of diphenylmethane in the presence of a metal catalyst, such as copper naphthenate. This reaction allows for the efficient conversion of diphenylmethane to benzophenone through a controlled oxidation process.
Another method relies on a Friedel-Crafts acylation , which involves reacting benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of an acid catalyst such as AlCl₃ (aluminum chloride) . This reaction is widely used in organic chemistry to introduce a carbonyl group into an aromatic structure.
Finally, a third method involves using phosgene as a reagent to obtain benzophenone from benzene. However, due to the high toxicity of phosgene, this method is used less and less in the modern chemical industry.
Natural formation and degradation
Although benzophenone is primarily of synthetic origin, it can also form naturally through the degradation of other chemical compounds. A recent study has shown that octocrylene , an ingredient commonly used in sunscreens and some cosmetic products, can degrade over time into benzophenone through oxidation.
This discovery has raised concerns about prolonged consumer exposure to this molecule, particularly through the use of cosmetics containing octocrylene. This phenomenon of spontaneous degradation may also explain the presence of benzophenone in certain marine environments, where it contributes to the pollution of aquatic ecosystems.
Due to its chemical properties and transformation potential, benzophenone is a ubiquitous molecule in various industrial applications . However, its stability and ability to accumulate in the environment warrant strict monitoring through specialized laboratory analyses.
2. What are the uses of benzophenone?
Benzophenone is a versatile compound used in various industrial sectors due to its photoprotective, stabilizing, and reactive properties . Its main role is to prevent the degradation of products exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which explains its presence in many consumer products and technical materials.
Use in the cosmetics industry
Benzophenone is widely used in cosmetic products because of its ability to absorb UV rays and protect formulations from light-induced degradation. It is present in several types of products:
- Sunscreens : used as a UV filter , benzophenone (especially benzophenone-3 or oxybenzone) protects the skin against the harmful effects of solar radiation.
- Perfumes and eau de toilette : preserves the stability of volatile compounds and prevents alteration of fragrances due to exposure to light.
- Soaps and lotions : prevents oxidation of active ingredients and prolongs the shelf life of formulations.
However, due to its potential to disrupt the endocrine system , its use is now subject to restrictions, particularly in Europe, where the maximum permitted concentration in cosmetics has been reduced from 10% to 6% for some products, and to 0.5% for others .
Role in the inks and varnishes industry
Benzophenone is an essential component of UV inks and printing varnishes . Thanks to its ability to absorb ultraviolet radiation, it allows for:
- Accelerate the polymerization of inks and varnishes under UV exposure, thereby improving the resistance and durability of prints.
- Prevent yellowing of prints exposed to sunlight.
- Stabilize colors by preventing their premature degradation.
This property makes it a key additive in the offset, flexographic, and gravure printing . However, concerns about the migration of benzophenone from packaging into food have led to stricter regulations, imposing rigorous testing to ensure the safety of printed materials in contact with food.
Applications in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical sectors
In the pharmaceutical , benzophenone is a chemical intermediate used in the synthesis of several classes of drugs. It is involved in the production of:
- Analgesics and anti-inflammatories .
- Antifungal medications.
- Photosensitizing compounds used in dermatology.
In agrochemistry , benzophenone is involved in the manufacture of certain pesticides and herbicides , serving as a structural basis for various active compounds intended to protect crops against pests and diseases.
Stabilization of plastic and polymer packaging
One of the most strategic uses of benzophenone is as a UV stabilizer in polymers and plastics. It is added to materials to:
- Preventing photodegradation of plastics exposed to sunlight.
- Extending the lifespan of packaging and plastic materials.
- Preventing yellowing and brittleness of polymers under the effect of UV rays.
transparent materials such as PET (polyethylene terephthalate) or PVC without risking rapid deterioration due to UV exposure.
However, the potential migration of benzophenone into food has raised concerns about its potential toxicity . Migration tests are now required for materials that come into contact with food, in accordance with EC Regulation No. 1935/2004 .
Applications in organic chemistry and in the laboratory
In chemistry, benzophenone is used for its reactive properties in several laboratory processes:
- Deoxygenating agent for aprotic solvents: in association with metallic sodium, it forms a dark purple radical that allows the removal of dissolved oxygen and ether peroxides in solvents before distillation.
- A pioneer in the synthesis of new compounds in organic chemistry, particularly in the manufacture of complex aromatic derivatives.
Thanks to these applications, benzophenone plays a key role in the preparation of ultra-pure solvents , necessary for fine chemistry experiments and pharmaceutical industries.
Presence in everyday products and controversies
In addition to its industrial uses, benzophenone is sometimes present in everyday consumer products , including:
- Cigarettes , where it is used as an additive.
- Anti-aging shampoos and creams , in which it may be derived from the degradation of octocrylene .
However, its suspected toxicity has led to stricter regulations and increased awareness among manufacturers, who are seeking to gradually replace this ingredient with less controversial alternatives.
Benzophenone's versatility explains its widespread use in several industries, but growing concerns about its health and environmental risks are prompting increased monitoring and the adoption of safer solutions.
Are you looking for an analysis?

3. What are the dangers of benzophenone for health and the environment?
The use of benzophenone in many industrial sectors raises major concerns due to its potentially toxic effects on human health and the environment. Classified as an endocrine disruptor and probable carcinogen , it is subject to increasingly strict regulations to limit its impact.
Effects on human health
Classified as a probable carcinogen
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) has classified benzophenone in Group 2B , meaning it is a possible human carcinogen . This classification is based on sufficient evidence of its carcinogenic potential in animals.
Studies conducted on rodents exposed to benzophenone have shown:
- An increased risk of liver cancer and lymphomas.
- Abnormalities in cell proliferation , suggesting a tumor-promoting effect.
Although human studies are still limited, these results have led to restrictions on use in several countries, including the United States and Europe.
Endocrine disruption and hormonal effects
Benzophenone is suspected of acting as an endocrine disruptor , meaning it interferes with the normal functioning of the hormonal system. Several studies have shown that certain forms of benzophenone, particularly benzophenone-3 (BP3) , can:
- To mimic or block the action of sex hormones , particularly estrogens and androgens.
- To alter the development of the reproductive system , particularly in embryos and young children.
- Influencing fertility by altering sperm production and hormonal regulation in men.
These effects explain why European regulatory authorities have lowered the maximum permitted concentrations of benzophenone-3 in cosmetics, limiting its use in sunscreens and skincare products.
Skin toxicity and allergic reactions
Present in cosmetics and perfumes, benzophenone can cause skin irritation and allergic reactions, particularly when exposed to sunlight. These include:
- Contact dermatitis , characterized by redness and itching.
- Photoallergic reactions , where exposure to UV light worsens the skin's sensitivity to benzophenone.
Individuals with sensitive skin or a history of skin allergies should therefore avoid products containing benzophenones , especially benzophenone-3 (BP3), which is often found in sunscreens.
Environmental impact and ecological risks
Contamination of aquatic environments
One of the most concerning effects of benzophenone is its dispersal in the environment , particularly through rinse-off cosmetics (sunscreens, lotions, shampoos) which end up in wastewater. Traces of benzophenone have thus been found in:
- Surface waters (rivers, lakes, oceans).
- Aquatic sediments , where it can accumulate over the long term.
- Marine organisms , including fish and corals.
Toxicity to aquatic wildlife and destruction of coral reefs
Benzophenone-3 and other derivatives found in sunscreens are accused of contributing to the destruction of coral reefs . Several studies have shown that these compounds:
- They damage the DNA of corals , affecting their growth and reproduction.
- They cause coral bleaching , reducing their ability to survive.
- They interfere with the hormonal system of marine organisms , impacting their metabolism and reproduction.
Because of these effects, several countries and regions , such as Hawaii and some Caribbean islands , have banned the use of sunscreens containing oxybenzone (BP3) to protect coral reefs.
Migration from packaging to food
Benzophenone is used as a stabilizer in plastics and UV printing inks, particularly for food packaging . However, studies have revealed that this substance can migrate from packaging into food , thus posing a risk to human health.
This phenomenon is particularly worrying for:
- Fatty foods (oil, butter, chocolate) promote the extraction of contaminants.
- Products stored at high temperatures , where migration is amplified.
To limit these risks, EC Regulation No. 1935/2004 imposes migration tests on materials in contact with food.
Regulations and restrictions on use
In response to health and environmental concerns, several regulations have been put in place to limit exposure to benzophenone.
Restrictions in cosmetics (EU Regulation 2022/1176)
- Since January 2023The maximum permitted concentration of benzophenone-3 has been reduced:
- 6 % for face and hand sunscreens.
- 2,2 % for body products in spray or aerosol form.
- 0,5 % if used solely as a stabilizer.
These new restrictions aim to reduce skin absorption and limit hormonal and carcinogenic risks .
Prohibited in materials that come into contact with food
In the United States , the FDA has banned the use of benzophenone as a food additive due to its potential carcinogenicity . In Europe, EC Regulation No. 10/2011 sets migration limits to prevent food contamination by this substance.
Prohibited in certain ecologically sensitive areas
To protect coral reefs, several jurisdictions have adopted targeted bans on benzophenone-3 and other harmful UV filters:
- Hawaii and Palau : ban on sunscreens containing oxybenzone (BP3).
- Virgin Islands and Key West (Florida) : similar restrictions to preserve coral reefs.
Need to monitor for the presence of benzophenone
Given the risks associated with benzophenone, laboratory analyses are essential to monitor its presence and ensure product compliance. These analyses allow us to:
- Check the concentrations in cosmetics and food packaging.
- Controlling water and soil contamination.
- Ensure compliance with applicable regulations.
The use of advanced analytical methods , such as gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) , is essential to detect minute traces of benzophenone in various matrices .
Growing concerns about benzophenone are pushing the industry to seek safer alternatives , while strengthening controls to limit its impact on health and the environment.

4. What is the chemical reaction of benzophenone?
Benzophenone is an organic compound with varied chemical reactivity , primarily due to the presence of the ketone group (C=O) and its two benzene rings. Its chemical behavior allows it to be used in several industrial and laboratory reactions.
Reactive properties of benzophenone
Benzophenone is an aromatic ketone , meaning it has a carbonyl group (C=O) directly attached to two benzene rings. This structure gives the molecule specific chemical properties:
- Carbonyl group polarity : confers reactivity towards nucleophiles.
- Ability to form free radicals : in the presence of certain reagents such as sodium.
- High thermal stability : it does not easily decompose under the effect of heat.
- UV absorption : it is capable of absorbing specific wavelengths, making it a stabilizer for various materials.
Thanks to these characteristics, benzophenone is involved in several chemical reactions used in organic synthesis and laboratory analysis.
Reduction of benzophenone to benzyl alcohol
One of the most common reactions of benzophenone is its reduction to benzyl alcohol , which can be achieved by several reducing agents:
- Catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of Pd/C or Nor from Raney :
- Benzophenone + H₂ → Diphenylmethanol
- Chemical reduction with LiAlH₄ (Lithium aluminium hydride) :
- This method allows us to obtain a primary alcohol , by transforming the ketone group into an alcohol.
Benzophenone reduction is essential in the pharmaceutical industry, as it enables the production of synthetic intermediates for various drugs .
Formation of benzophenone-sodium radicals
In organic chemistry, benzophenone is commonly used as a deoxygenating agent for aprotic solvents . This application is based on its ability to form a stable radical in the presence of metallic sodium :
- Benzophenone + Na → Benzophenone-sodium radical (dark purple)
This radical is a highly reactive species that can eliminate dissolved oxygen and ether peroxides present in solvents. This reaction is used to purify solvents such as:
- Toluene
- THF (tetrahydrofuran)
- Diethyl ether
The appearance of a violet color is a reliable indicator that all peroxides and traces of oxygen have been eliminated , thus guaranteeing the purity of the solvent used in chemical synthesis.
Reaction of benzophenone with nucleophiles
The carbonyl group of benzophenone can be attacked by nucleophiles to form new compounds. These reactions are commonly used in organic chemistry to obtain useful derivatives:
- Reaction with amines to form imines :
- Benzophenone + Primary amine → Imino-benzophenone
- Reaction with sodium cyanide (NaCN) to produce cyanohydrins :
- Benzophenone + NaCN → Benzophenone cyanohydrin
These derivatives are used in the synthesis of drugs and specialty chemicals .
Photoreactivity and free radical formation
A unique property of benzophenone is its ability to generate radicals under UV exposure . This reaction is essential in industrial applications such as UV varnishes and printing inks .
- Under UV exposure, benzophenone absorbs light energy and goes into an excited state .
- This excited state allows the formation of radicals capable of initiating polymerization reactions.
This property explains why benzophenone is widely used as a photoinitiator in the printing and coating industries.
Oxidation of benzophenone to benzoic acid
Under certain conditions, benzophenone can undergo oxidation, particularly by strong oxidizing agents such as potassium permanganate (KMnO₄), to form benzoic acid :
- Benzophenone + KMnO₄ → Benzoic acid + By-products
This reaction is important in the perfume and flavor industry, as benzoic acid is a precursor to many odoriferous compounds.
Spontaneous formation by degradation of octocrylene
A recently discovered phenomenon is the formation of benzophenone by aging of octocrylene , a UV filter used in sunscreens and cosmetic products.
- Over time, under the effect of oxidation and UV radiation , octocrylene can decompose to release benzophenone.
- This phenomenon is concerning because it leads to indirect exposure to benzophenone in cosmetics, even if it is not initially present in the formulation.
This discovery has reinforced the need to monitor the presence of benzophenone in sunscreens and skincare products through laboratory analysis .

5. Why analyze benzophenone in the laboratory?
Benzophenone is a compound with multiple uses , but its effects on health and the environment require rigorous control. Laboratory analyses allow for its detection , the assessment of its impact , and verification of current regulations
Need to monitor for the presence of benzophenone
The presence of benzophenone in cosmetics, food packaging, and the environment warrants in-depth analysis for several reasons:
- Ensuring regulatory compliance : maximum permitted concentrations are increasingly restricted by legislation.
- Identifying benzophenone migration : some plastic packaging can contaminate food , leading to unintentional exposure.
- Monitoring environmental accumulation : the presence of benzophenone in water , soils and living organisms can have serious ecological consequences .
Analytical testing therefore allows manufacturers to guarantee the safety of their products and avoid the risks of non-compliance .
Analysis of benzophenone in cosmetics
Cosmetic products, particularly sunscreens and lotions , are a major source of benzophenone exposure . It is essential to check:
- The concentration of benzophenone-3 (BP3) : its presence is permitted, but within strict limits (6% in certain creams, 2.2% in body products, 0.5% if used as a stabilizer).
- Formulation stability : the degradation of certain ingredients can generate benzophenone over time, requiring precise monitoring.
- Compliance with EU and FDA regulations : analytical testing ensures that products meet international standards .
Migration study in food packaging
inks and varnishes used for printing food packaging may contain benzophenone. Under certain conditions (temperature, prolonged contact), it can migrate into food .
Specialized laboratories therefore carry out migration tests , in accordance with EC Regulation No. 1935/2004 , to verify that:
- The packaging does not release benzophenone beyond the permitted levels.
- The materials used are safe for the consumer.
- The effects of heat and humidity on migration are controlled.
These tests are essential to prevent unintentional contamination of food products.
Detection of benzophenone in the environment
Benzophenone and its derivatives are widely present in the environment due to their extensive use and chemical persistence . Environmental analyses allow us to measure their concentration in:
- Wastewater and rivers : Sunscreen rinsed off in the shower can contaminate sewage systems.
- Sediments and soils : industrial discharges or natural degradation of printed plastics can release benzophenone.
- Aquatic organisms : traces of benzophenone have been detected in some fish and corals, raising concerns about bioaccumulation.
These analyses are essential to assess the ecological impact of benzophenone and to implement strategies to reduce its use .
The need to verify the purity of solvents in the laboratory
In organic chemistry, benzophenone is used to dry and deoxygenate solvents , particularly in combination with metallic sodium . However, the presence of impurities can alter the reactivity of solvents and distort laboratory experiments.
The tests performed on the solvents allow us to:
- Measure the residual benzophenone concentration.
- Ensuring the quality and reproducibility of chemical reactions.
- Eliminate traces of peroxides and oxygen that may interfere with certain syntheses.
These analyses are crucial for research laboratories and the pharmaceutical industry .
Analytical tools and techniques used in the laboratory
Benzophenone analysis relies on advanced techniques that allow for precise quantification in various matrices (cosmetics, packaging, water, solvents). Among the methods used are:
- Gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS) :
- Detects and quantifies benzophenone in sunscreens, food packaging and solvents .
- trace analysis and migration control.
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) :
- Allows for the analysis of benzophenone in complex matrices , such as lotions and toilet waters.
- Suitable for liquid and semi-solid samples.
- UV-Visible spectrophotometry :
- It exploits benzophenone's ability to absorb UV rays .
- Used for rapid and qualitative analyses .
- Migration tests :
- They check the amount of benzophenone transferred from packaging into food.
- European (EC 1935/2004) and American (FDA) standards .
These methods allow for the reliable detection and regulatory monitoring of benzophenone in various products.

6. How does YesWeLab support manufacturers in the analysis of benzophenone?
Faced with increasingly stringent regulations and health and environmental concerns related to benzophenone, manufacturers need reliable analytical solutions to guarantee the compliance of their products. YesWeLab , thanks to its network of over 200 partner laboratories , offers analyses tailored to the needs of companies in various sectors: cosmetics, food processing, packaging, chemicals, and the environment .
A digital platform to centralize analyses
YesWeLab facilitates access to laboratory services by providing an innovative digital platform that enables:
- Centralization of analytical needs : consultation of a catalogue of more than 10,000 analyses .
- Real-time tracking of samples : complete traceability from the sending of samples to the receipt of results.
- Access to a network of specialist laboratories : accredited ISO 17025 and COFRAC .
- Optimized time management : reduced waiting time thanks to the allocation of analyses to the most suitable and available laboratory .
This approach greatly simplifies the analytical process for businesses, allowing them to save time and ensure their regulatory compliance .
Technical expertise for benzophenone analysis
YesWeLab collaborates with laboratories specializing in the detection and quantification of benzophenone and its derivatives. Services cover several areas:
Analysis of cosmetic products
YesWeLab offers specific analyses to check for the presence of benzophenone-3 (BP3) and other derivatives in cosmetic products:
- Dosage of benzophenone-3 in sunscreens to ensure compliance with regulatory limits (6%, 2.2%, 0.5% depending on the product).
- Analysis of lotions and perfumes to identify traces of benzophenone that may come from the degradation of ingredients such as octocrylene .
- Stability study of formulations containing UV filters.
Migration tests in food packaging
Plastic, paper, cardboard, and printed film packaging can contain benzophenone, particularly through UV inks used in the printing industry. YesWeLab performs:
- Specific migration tests to assess whether benzophenone migrates from packaging into food.
- Analyses compliant with CE and FDA standards , based on advanced chromatographic tests (GC-MS, HPLC) .
- Regulatory compliance audits to ensure that packaging meets the safety thresholds set by the EU .
Environmental analyses and wastewater monitoring
Benzophenone and its derivatives can contaminate aquatic environments , particularly due to industrial and cosmetic discharges . YesWeLab offers:
- Sampling and analysis of surface and groundwater to detect the presence of benzophenone.
- Bioaccumulation tests in aquatic organisms to assess environmental impact.
- Studies of persistence and degradation in water and sediments.
7. Case studies and collaboration with industries
YesWeLab already supports many manufacturers to help them identify and limit the presence of benzophenone in their products.
Cosmetics industry: UV filter compliance
A sunscreen manufacturer has asked YesWeLab to analyze the benzophenone-3 content in its formulations.
Thanks to the tests carried out:
- He was able to adjust the concentrations to comply with the new European standards.
- He identified an involuntary formation of benzophenone due to the degradation of octocrylene .
- He optimized his formulations by replacing some UV filters with safer alternatives .
Food industry: packaging migration
A food packaging manufacturer wanted to verify the compliance of its materials with regard to the risks of benzophenone migration .
The analyses carried out allowed us to:
- Confirm that some printed cardboard packaging released traces of benzophenone.
- Propose alternatives to UV inks and protective varnishes to limit migration.
- Implement regular monitoring of packaging to ensure regulatory compliance.
Environmental analysis: monitoring water contamination
A company in the chemical sector called upon YesWeLab to measure the presence of benzophenone in its industrial waste .
The results led to:
- The implementation of specific treatments to limit the presence of contaminants in wastewater.
- Increased monitoring of emissions in order to anticipate possible violations of environmental regulations.