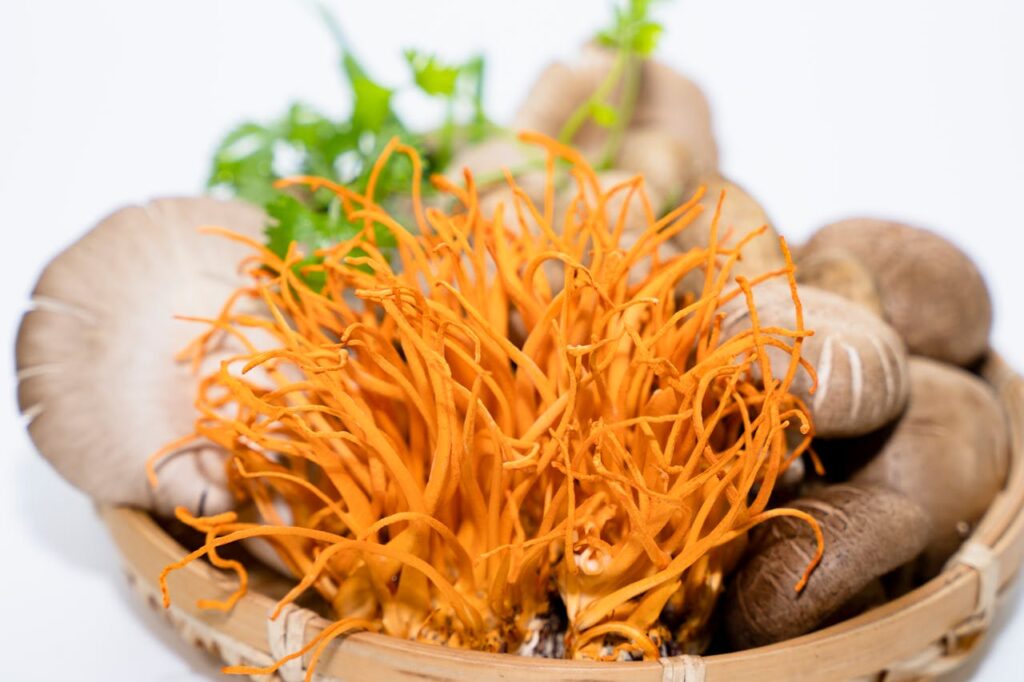
Cordycepin, or 3'-deoxyadenosine, is a bioactive compound isolated from mushrooms of the genus Cordyceps , recognized for its anticancer, antiviral and immunomodulatory properties. This molecule of growing interest in the nutraceutical, cosmetic and pharmaceutical sectors also represents a major analytical challenge for laboratories. In this article, we analyze in detail its chemical structure, biological effects, industrial applications and the regulatory standards governing its use. Emphasis is placed on laboratory assay methods – notably by HPLC and LC-MS/MS Cordyceps -based extracts standardized in cordycepin.
Table of Contents
What is cordycepin? Definition, origin and chemical structure
Definition and chemical designation
Cordycepin, identified under the CAS number 73-03-0, is a naturally occurring molecule belonging to the family of nucleoside analogues. Its full chemical name is 3'-deoxyadenosine , which means that it is a derivative of adenosine without the hydroxyl group (–OH) in the 3' position of the ribose. This slight structural modification has major consequences for its biological activity: by substituting for adenosine in certain biochemical processes, cordycepin disrupts RNA synthesis and cell proliferation.
From a physicochemical point of view, cordycepin is a polar molecule, poorly soluble in conventional organic solvents but soluble in water, which facilitates certain extraction and dosage methods. Its molar mass is 251.24 g/mol , and its gross formula is C10H13N5O3 . It appears as a white or slightly yellowish powder, sensitive to light and heat.
Natural origin: a unique fungal compound
Cordycepin is mainly produced by two species of entomopathogenic fungi: Cordyceps militaris and Cordyceps sinensis . These mushrooms belong to the Cordycipitaceae family and are well known in traditional Chinese medicine for their revitalizing properties.
The life cycle of Cordyceps sinensis is particularly fascinating. This parasitic fungus develops in the larvae of butterflies of the genus Thitarodes . Once infected, the larva is gradually colonized by the fungal mycelium, until it emerges as a small fruiting body (carpophores) that emerges from the head of the mummified caterpillar. This wild form is extremely rare and expensive, which explains why Cordyceps militaris , which is easier to cultivate in the laboratory, is today the main industrial source of cordycepin.
There are also cultivated forms from specific strains such as Paecilomyces hepiali , a mycelial species isolated from C. sinensis , which allows large-scale production while guaranteeing a chemical composition close to that of the wild mushroom.
Importance of cordycepin in research and industry
Due to its structure similar to adenosine, cordycepin acts as a metabolic decoy, making it a potent inhibitor of RNA transcription . This mechanism gives it a variety of highly sought-after biological properties: inhibition of cell proliferation, activation of the immune response, regulation of inflammatory pathways, and blocking of viral replication.
These properties explain the growth of its use in the following sectors:
- nutraceutical : health products based on medicinal mushrooms,
- cosmetics : anti-aging formulas rich in antioxidant compounds,
- pharmaceutical : research into new anticancer or antiviral therapies.
Cordycepin is also used as an analytical marker Cordyceps extracts . Accurate quantification of this molecule is essential to ensure the effectiveness of products sold as dietary supplements or for topical use, hence the importance of laboratory analyses, which we will detail in the following sections.

Biological properties and mechanisms of action of cordycepin
Cordycepin has been studied for decades for its remarkable pharmacological effects. Due to its unique structure, it interferes with several key cellular processes, giving it antitumor, antiviral, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. These effects have been demonstrated in numerous in vitro and in vivo models and are currently the subject of clinical trials in several therapeutic areas.
Main mechanism: inhibition of RNA synthesis
The most studied mode of action of cordycepin is its ability to interfere with RNA synthesis . When it is phosphorylated in cells to 3'-deoxyadenosine triphosphate (3'-dATP), it can be incorporated in place of adenosine into the forming RNA chain. However, the absence of the 3' hydroxyl (–OH) group prevents normal chain elongation, thus interrupting RNA transcription .
This inhibition of transcription results in:
- stopping cell proliferation,
- disruption of RNA-dependent metabolic pathways,
- the induction of apoptosis (programmed cell death) in certain cells.
This mechanism is particularly effective against cancerous or virus-infected cells, which exhibit high transcriptional activity.
Documented anticancer effects
Numerous studies have demonstrated the antitumor of cordycepin on several types of cancer lines: leukemia, breast cancer, liver cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, etc. Among the effects observed:
- inhibition of cell proliferation,
- induction of apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway,
- reduction in the expression of genes linked to cell survival (Bcl-2, survivin),
- inhibition of tumor migration and invasion.
A study published in Cancer Letters (2019), for example, showed that cordycepin inhibited the growth of liver cancer cells by blocking the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, which is essential for cell survival.
The major challenge lies in its bioavailability: cordycepin is rapidly degraded in the body by adenosine deaminase (ADA). Encapsulated formulations or those associated with ADA inhibitors are being studied to improve its stability in vivo.
Antiviral and anti-inflammatory activity
Cordycepin also has antiviral . By disrupting viral RNA transcription or inhibiting certain viral RNA polymerases, it limits the replication of single-stranded RNA viruses. Research is underway on its effectiveness against viruses such as hepatitis B, certain coronaviruses, and herpes viruses.
In parallel, cordycepin acts as an inflammation modulator . It inhibits the production of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6 or COX-2, and reduces the expression of transcription factors such as NF-κB. This dual effect – antiviral and anti-inflammatory – is particularly interesting in contexts of chronic infection or autoimmunity.
Immunomodulatory properties
Cordycepin stimulates certain responses of the innate and adaptive immune system :
- activation of macrophages,
- increased phagocytosis,
- regulation of cytokine production (IL-2, IFN-γ),
- stimulation of T lymphocytes.
These properties could explain its traditional use as a tonic in Chinese medicine, but they are also of interest to clinical research in the field of anticancer immunotherapy or immunostimulation in immunocompromised people.
Antioxidant and neuroprotective activity
Cordycepin is also known for its antioxidant properties , which help neutralize free radicals and reduce cellular oxidative stress. This mechanism helps prevent premature aging of cells and protect tissues against oxidative damage.
Some studies also suggest a neuroprotective in cases of cellular stress, neuronal inflammation, or progressive degeneration. These properties are of particular interest to researchers in the fields of cognitive decline prevention and support in cases of neurodegenerative diseases.
In summary, cordycepin acts on several biological fronts: RNA transcription, cell signaling, inflammation, immunity and oxidative stress. This versatility makes it a molecule of priority interest in the fields of therapeutic research, but also a crucial analytical target for manufacturers who wish to guarantee the quality, stability and safety of their Cordyceps .
Are you looking for an analysis?

Applications of cordycepin in industry
Cordycepin is attracting increasing attention from healthcare, cosmetics, and food professionals for its promising biological effects. Its versatility allows it to be incorporated into various finished products, including dietary supplements, cosmetic active ingredients, or drug candidates under development. However, these applications require rigorous control of the quality and concentration of the active ingredient, which necessitates precise and standardized laboratory analyses.
Food supplements and nutraceuticals
The market for medicinal mushroom supplements is booming, with increasing demand for natural products with energizing, immunostimulating, or adaptogenic effects. Cordycepin, extracted mainly from Cordyceps militaris , is a key quality marker in these formulations.
Claimed uses
Manufacturers highlight several potential effects:
- energy boost and fatigue reduction,
- improved vitality and physical recovery,
- immune system support,
- natural antioxidant and anti-aging effect.
These claims, while popular, have not yet been validated by the EFSA in Europe. However, Health Canada recognizes the safe use of Cordyceps provided that specific dosages are followed (e.g., 1.5 to 3 g/day of dehydrated powder). Cordycepin, as an active biomarker, plays a key role in the standardization of extracts.
Available dosage forms
Cordycepin products come in several forms:
- raw powder (whole mushroom dehydrated then ground),
- capsules containing standardized powder or extracts,
- liquid extracts (water, alcohol, glycerin),
- CS-4 form : mycelium grown industrially from Paecilomyces hepiali , rich in compounds similar to those of Cordyceps sinensis .
The most reliable products are those titrated in cordycepin (≥ 0.03%) and/or cordycepic acid (≥ 7%) , two markers frequently analyzed in the laboratory to guarantee the potency and stability of the extract.
Cosmetic
The inclusion of cordycepin in cosmetic products is explained by its antioxidant, soothing, and revitalizing properties. This ingredient is used in treatments intended for:
- to reduce the signs of aging (wrinkles, loss of elasticity),
- to protect the skin from oxidative stress ,
- to promote cell regeneration .
Application examples
Cordycepin can be incorporated into:
- anti-aging serums or moisturizers,
- restorative care for sensitive skin or skin exposed to pollution,
- formulations targeting complexion radiance and skin regeneration .
The addition of cordycepin to these products must be accompanied by rigorous testing: dosage of the active molecule, stability tests , evaluation of compatibility with other active ingredients, and skin safety tests . Specialized laboratories often carry out LC-MS/MS or HPLC analyses to ensure the actual presence of cordycepin in the final formula.
Pharmaceutical and clinical research
Cordycepin is also being studied for more advanced therapeutic applications, particularly in the fields of oncology, rheumatology or viral diseases.
Indications explored
Several clinical trials are underway to evaluate:
- the effect of cordycepin as an adjuvant to chemotherapy , to increase the sensitivity of tumor cells,
- its action on osteoarthritis , in particular to slow down the degradation of articular cartilage ,
- its antiviral potential against RNA viruses, including certain strains of influenza and hepatitis.
This research is based on previously studied biological mechanisms (inhibition of RNA synthesis, induction of apoptosis, modulation of the immune response). However, the rapid degradation of cordycepin in vivo remains a major obstacle. Solutions are being considered, such as liposomal encapsulation or combination with enzyme inhibitors (ADA inhibitors).
Regulatory framework
In the pharmaceutical context, cordycepin is still considered an active ingredient in development , subject to rigorous evaluations:
- chemical stability,
- pharmacokinetic profile,
- safety and efficacy in animal and human models.
Any attempt to register as a pharmaceutical substance requires standardized laboratory analyses , carried out under conditions conforming to ISO 17025 and, if applicable, GMP/GLP (Good Manufacturing or Laboratory Practices) .

Cordycepin and regulations: what the law says
Despite its many documented biological properties, cordycepin remains a strictly regulated molecule. Depending on its use—food supplement, cosmetic ingredient, or pharmaceutical active ingredient—legal requirements vary from country to country. This variability requires manufacturers to be constantly vigilant and ensure rigorous traceability of their cordycepin-containing products.
Regulatory status in Europe
In the European Union, cordycepin is not permitted as an additive or isolated active ingredient in food supplements. However, it may occur naturally in Cordyceps sinensis or Cordyceps militaris , provided that these extracts are sourced from a safe, documented source that complies with food safety requirements .
Cordyceps extracts , the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) requires:
- the full declaration of active ingredients , including cordycepin, adenine and cordycepic acid,
- the assessment of heavy metal levels , in particular lead, arsenic and cadmium,
- toxicity data , particularly in the case of health claims.
Furthermore, the use of Cordyceps militaris or cultivated forms such as Paecilomyces hepiali (strain CS-4) is not permitted in all EU countries. Some Member States classify them as novel foods under Regulation (EU) 2015/2283, which requires a prior authorisation procedure, including a complete scientific dossier .
Recognition in Canada and the United States
Conversely, in Canada , cordycepin is recognized as an active component present in Cordyceps-based natural health products. Health Canada has defined specific dosage limits:
- dehydrated powder : 1.5 to 3 g per day,
- decoction : up to 9 g/day of dry matter,
- CS-4 form : 1 to 2 g per day.
These thresholds are intended to minimize the risk of side effects while ensuring plausible efficacy. Manufacturers must provide laboratory analyses confirming the presence of active ingredients (cordycepin, cordycepic acid) and the absence of contaminants.
In the United States , regulation depends on the product's status. If cordycepin is included in a dietary supplement , it falls under the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) . However, since it is sometimes extracted from mushrooms classified as "herbs of traditional Chinese medicine," it can also be considered a botanical product , which requires specific regulatory positioning, particularly in the case of therapeutic claims.
Supervision in cosmetics and external use
In cosmetic products, cordycepin may be used as a crude mushroom extract , provided that the supplier demonstrates:
- safe plant or fungal origin ,
- the absence of direct pharmacological effect on the skin,
- results of microbiological and toxicological analyses .
According to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 , cosmetic ingredients must be assessed for their safety, via a Cosmetic Product Safety Report (CPSR) . This report includes:
- the physicochemical characterization of the extracts,
- concentrations of active ingredients (including cordycepin),
- skin or ophthalmological tolerance tests.
No health claims may be made for a cosmetic product containing cordycepin. Terms used must be limited to general cosmetic effects (conditioning, moisturizing, antioxidant protector, etc.).
Need for rigorous analytical and documentary control
Regulatory compliance necessarily involves the implementation of reliable laboratory analyses , allowing:
- identify and quantify cordycepin in extracts,
- detect the presence of contaminants , including heavy metals, residual solvents, pesticides or microorganisms,
- document the botanical or mycological origins of the raw material,
- validate product claims in relation to local regulations.
These controls are required not only to meet the requirements of regulatory authorities, but also to protect the consumer against falsified or under-dosed products, which are common on the market for plant and fungal extracts.
In short, cordycepin can only be used in an industrial setting if it complies with strict regulatory standards , which vary depending on the region and the use. This compliance requires complete traceability , certified laboratory analyses and constant vigilance regarding regulatory developments. Any company wishing to market a product containing cordycepin therefore has every interest in collaborating with a laboratory expert in the dosage of plant and fungal extracts, compliant with ISO 17025 requirements and good analytical practices.
How to analyze cordycepin in the laboratory?
Cordycepin analysis is essential to ensure the quality, authenticity and compliance of Cordyceps . Whether for a dietary supplement, a cosmetic product or a pharmaceutical formulation, the precise dosage of cordycepin helps to secure products and ensure their effectiveness. This analysis is based on validated methods, used in laboratories accredited according to ISO 17025 standards, and adapted to complex matrices.
HPLC/UV method: the reference for cordycepin measurement
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with UV detection is currently the standard method for the quantitative analysis of cordycepin in mushroom extracts. This technique relies on the separation of the constituents of a sample on a chromatographic column, followed by their detection at a specific wavelength.
Advantages of the method:
- High sensitivity : allows cordycepin to be detected at very low concentrations (LOQ around 10 mg/kg).
- Good specificity : efficient separation between cordycepin, adenine, adenosine and other components of the mushroom.
- Method validated in many laboratories for quality control applications.
The wavelength used for detection is typically 254 nm , which corresponds to the maximum absorption peak of cordycepin. Sample preparation may include extraction with water or ethanol, followed by filtration or centrifugation to remove solid particles.
LC-MS/MS mass spectrometry: for complex matrices
In cases where the matrix is particularly complex (plant mixtures, concentrated dry extracts, cosmetic formulations), mass spectrometry coupled with liquid chromatography (LC-MS/MS) is preferred.
This technique offers even higher specificity than HPLC/UV, thanks to the analysis of the characteristic ions of cordycepin, which allows:
- detection without interference from other compounds,
- quantification even at trace levels (< 1 mg/kg),
- a multi-residue analysis (possibility of simultaneously measuring several fungal components).
It is recommended in the following contexts:
- quality control of complex products (multi-ingredient capsules, enriched extracts),
- pharmacokinetic studies,
- investigations in the event of complaints or non-conformities.
Other possible techniques: direct UV, NMR, enzymatic titration
Other simpler or more specific techniques can be used depending on the objectives:
- UV/Vis spectrophotometry : used for rapid batch checks, but not very specific.
- Enzymatic titration : as part of rapid methods in industry (for example to differentiate adenosine from cordycepin in certain extracts).
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) : powerful but expensive method, mainly used in research or to validate standards.
Preparation of samples and matrices involved
Cordycepin analysis can be performed on various matrices:
- dried mushroom powders (Cordyceps militaris, sinensis),
- or glycerin extracts
- capsules or tablets,
- cosmetic formulas (creams, serums),
- injectable or experimental solutions in a research context.
Preparation steps include:
- grinding and homogenization of solid samples,
- solvent extraction (water, ethanol, methanol),
- membrane filtration (0.45 µm),
- possibly purification by SPE (solid phase extraction) before injection into a chromatograph.
Particular attention should be paid to temperature and light , as cordycepin is sensitive to oxidation and thermal degradation.
Analysis standards and accreditations
For the analysis results to be acceptable to health authorities and industrial customers, they must be carried out according to the following standards:
- ISO 17025 standard : guarantees the competence of testing laboratories,
- COFRAC accreditation (in France) or equivalent depending on the country,
- validation of analytical methods (linearity, precision, specificity, LOD/LOQ, repeatability).
Laboratories must also provide a complete analysis report , stating the method used, the quantified results (in mg/kg or mg/g), the limit of quantification and compliance with product specifications.

Focus YesWeLab: an analytical partner for your cordyceps extracts
Cordycepin analysis requires advanced expertise and high-precision laboratory equipment. For nutraceutical, cosmetic, or animal health manufacturers, working with a trusted partner is essential to ensure the quality and compliance of Cordyceps extracts . This is precisely what YesWeLab , a company specializing in multi-sector analytical services, which relies on a network of more than 200 accredited partner laboratories across France and Europe.
An expert network dedicated to plant and fungal extracts
YesWeLab collaborates with highly specialized laboratories in the analysis of natural products, in particular:
- extracts of medicinal mushrooms ,
- plant raw materials , including bioactive ingredients such as cordycepin, cordycepic acid, adenosine or beta-glucans,
- finished nutraceutical products ( capsules, powders, liquid extracts),
- cosmetic formulations incorporating Cordyceps extracts .
Thanks to this network, YesWeLab is able to offer tailor-made analyses according to the matrices and regulatory requirements of each sector.
Types of matrices analyzed:
- Cordyceps militaris or sinensis powder,
- hydroalcoholic or glycerin extracts,
- capsules or tablets,
- creams, serums and topical treatments,
- multi-ingredient food supplements.
The results are delivered with a complete analysis report , including the following data:
- cordycepin concentration in mg/kg or percentage,
- dosage method used,
- limit of detection and quantification (LOD/LOQ),
- compliance with current standards (e.g.: ISO 17025, COFRAC).
Regulatory support and sector compliance
Beyond the analytical service, YesWeLab offers regulatory support on the following issues:
- compliance with European regulations (INCO, Novel Food, cosmetic regulation EC 1223/2009),
- validation of nutritional and health claims,
- preparation of registration or marketing files,
- adaptation of analytical protocols according to the requirements of EFSA, Health Canada or the FDA.
YesWeLab can also advise you on the choice of extract type (CS-4, fruiting body, mycelium), batch standardization, and selection of reliable suppliers.
A digital platform to simplify analysis management
One of YesWeLab's major assets is its all-in-one digital platform , designed to facilitate the management of your analytical projects:
- quick search among more than 10,000 available services,
- online ordering of customized analyses,
- real-time monitoring of sample progress,
- secure receipt of results , automatic archiving,
- complete traceability of all operations.
This solution allows companies to centralize all of their analytical needs , reduce execution times and optimize the compliance of their products.
Why use YesWeLab for your cordycepin analyses?
ISO 17025 and COFRAC certified laboratories .
✔️ Analysis of cordycepin according to validated methods (HPLC, LC-MS/MS).
✔️ Possibility of testing several fungal compounds in a single service.
✔️ Tailor-made regulatory support.
✔️ Easy tracking via an intuitive digital platform.
✔️ Fast turnaround times and guaranteed quality results.
Cordyceps -based dietary supplement ? Do you want to validate a standardized cordycepin extract for a cosmetic or pharmaceutical product? YesWeLab is your leading analytical partner to secure your formulations and ensure their compliance.
Contact us today for a personalized quote or online analysis catalog



