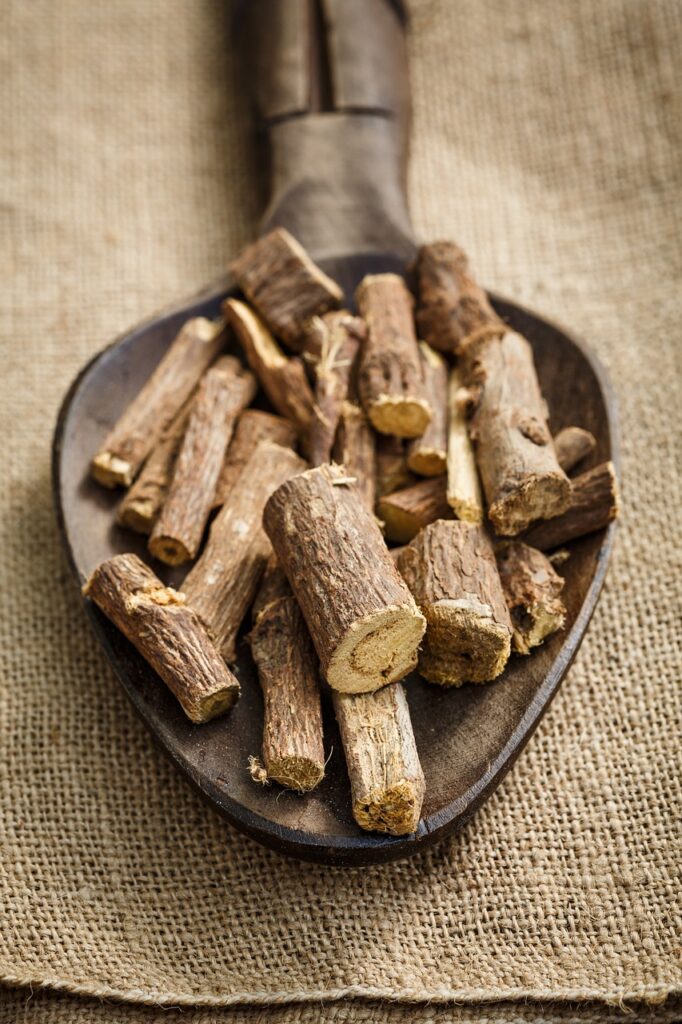
Glycyrrhizic acid, also known as glycyrrhizin, is a bioactive compound extracted from the roots of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra). This active ingredient is renowned for its numerous applications, ranging from traditional medicine to the food and cosmetic . Thanks to its unique properties, glycyrrhizic acid has garnered increasing interest in scientific research and industrial formulations.
1. Introduction to glycyrrhizic acid
Origin and chemical structure
Glycyrrhizic acid belongs to the saponin family, a class of glycosides that play an important role in biological interactions.
- Chemical structure : It consists of a triterpenic aglycone (glycyrrhetinic acid) linked to two molecules of glucuronic acid.
- Origin : Primarily extracted from the roots of licorice, a plant in the Fabaceae family, cultivated in regions such as Central Asia, China and the Mediterranean.
Physical and chemical properties
The physicochemical characteristics of glycyrrhizic acid make it a versatile compound.
- Solubility : Insoluble in pure water, but soluble as an ammonium salt at pH > 4.5.
- Sweetening power : Its sweet flavor is 30 to 50 times more intense than that of sucrose, although its sweet taste is slightly delayed and persistent, with a characteristic aftertaste.
- Stability : Relatively stable at moderate temperatures and pH variations, which favors its use in different formulations.
Historical and modern applications
Glycyrrhizic acid has been used since ancient times for its medicinal benefits and unique sweet taste.
- Traditional applications : Used as a remedy in Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine to treat conditions such as respiratory and digestive disorders.
- Modern uses : Today, it is used in the food industry as a natural sweetener, in cosmetics for its soothing properties, and in medicines for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
This introduction lays the groundwork for exploring in detail the multiple properties and uses of glycyrrhizic acid, which will be developed in the following sections.
2. The properties of glycyrrhizic acid
Biological properties
Glycyrrhizic acid is a bioactive compound with numerous therapeutic properties.
Anti-inflammatory
- Glycyrrhizic acid inhibits the action of the enzyme 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2, thereby increasing the availability of active cortisol in the body. This mechanism allows it to effectively reduce inflammation.
- Use: It is incorporated into topical creams to relieve redness, itching and skin inflammation, such as erythema or pruritus.
Antimicrobial and antiviral
- Glycyrrhizic acid has been shown to inhibit the growth of certain bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus, and viruses, such as the hepatitis C virus.
- These properties are used in medical formulations to treat skin infections and sore throats.
Sweetening and adaptogenic effect
- With a sweetening power 30 to 50 times greater than that of sucrose, glycyrrhizic acid is used in the food industry as a natural sweetener.
- It also acts as an adaptogen, helping the body to better resist physical and environmental stressors.
Physicochemical properties
Glycyrrhizic acid has remarkable physicochemical characteristics that favor its use in various sectors.
Solubility and stability
- Insoluble in pure water, glycyrrhizic acid becomes soluble as an ammonium salt at pH above 4.5.
- Its chemical stability makes it an ideal ingredient for long-term formulations in food and cosmetic products.
Antioxidant capacity
- By acting as a free radical scavenger, glycyrrhizic acid protects cells and DNA from oxidative damage. This ability is exploited in antioxidant cosmetics and anti-aging skincare products.
Impact on flavor
- Although sweet, glycyrrhizic acid has a characteristic and persistent aftertaste. This property is used to mask bitter flavors in pharmaceutical and food formulations.
Risks associated with excessive consumption
Despite its many benefits, glycyrrhizic acid can pose risks when consumed in excess.
High blood pressure
- Inhibition of the 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzyme can lead to excessive sodium and water retention, causing an increase in blood pressure.
Recommendations for intake
- The recommended daily intake (ADI) is limited to 100 mg/day to avoid adverse effects. Food labels must clearly indicate its presence in products.
3. Applications of glycyrrhizic acid in different sectors
Use in the cosmetics industry
Glycyrrhizic acid is a prized ingredient in cosmetic products due to its benefits for the skin.
Skincare for sensitive and reactive skin
- Thanks to its anti-inflammatory and soothing properties, it is used in creams to reduce redness, tightness and irritation.
- Studies show that it inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, thus offering an effective solution for reactive skin.
Skin lightening and anti-aging products
- Glycyrrhizic acid helps to reduce pigment spots by inhibiting tyrosinase, a key enzyme in melanogenesis.
- Its antioxidant effect protects the skin from damage caused by free radicals, thus slowing down the appearance of wrinkles and sagging skin.
Specific applications
- Products concerned: sunscreens, anti-redness treatments, brightening serums, and after-sun lotions.
- Dosage: generally between 0.5% and 2% in cosmetic formulations.
Applications in the agri-food sector
In the food industry, glycyrrhizic acid is used primarily as a natural sweetener and flavor enhancer.
Natural sweetener
- With a sweetening power 30 to 50 times greater than that of sucrose, it is commonly used in confectionery and beverages.
- Examples: licorice-based chewing gum, flavored teas, and certain desserts.
Flavor enhancer
- Glycyrrhizic acid masks the bitterness of artificial sweeteners like saccharin, thus improving the flavor of products.
- It is also used in some tobacco products to balance the flavors.
Food regulations
- Although recognized as safe (GRAS status in the United States), its consumption is limited due to its potential impact on health, including the risk of hypertension.
- Labeling is mandatory to inform consumers of its presence in food products.
Medical and pharmaceutical applications
Glycyrrhizic acid is a key ingredient in several medical treatments and pharmaceutical formulations.
Anti-inflammatory properties
- Used in creams and ointments to treat skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and sunburn.
- Example: creams containing 0.15% glycyrrhetinic acid combined with other soothing agents.
Treatment of sore throats and oral conditions
- Present in lozenges to soothe throat inflammations.
- Protective and moisturizing effect for irritated mucous membranes.
Studies on antiviral properties
- Research indicates antiviral activity against the hepatitis C virus and other pathogens. This property is generating increasing interest for the development of new treatments.
Limitations and precautions in different applications
Although glycyrrhizic acid has notable advantages, some limitations must be taken into account.
Excessive consumption and side effects
- Food and medicinal applications require special attention to avoid hypertension and water retention.
Specific regulations
- Standards vary by region: for example, in Japan, consumption is limited to 200 mg/day, while the European Union recommends a limit of 100 mg/day.
Are you looking for an analysis?

4. Laboratory analyses for glycyrrhizic acid
Common analysis techniques
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
- Principle : This method is based on the separation of the components of a mixture using a chromatographic column and their detection by UV spectrophotometry.
- Application : To measure the concentration of glycyrrhizic acid in various matrices such as food supplements, cosmetic products or aromatic plants.
- Advantages : High precision and low detection limit (up to 10 ppm for some matrices).
Mass spectrometry
- Principle : Analysis of ions produced from glycyrrhizic acid molecules, allowing precise identification of its chemical structure.
- Application : Detection of traces in complex matrices such as plant extracts or pharmaceutical formulations.
UV-Vis spectrophotometry
- Principle : Measurement of the absorption of light by a glycyrrhizic acid solution at specific wavelengths.
- Application : Rapid estimation of concentration in food or cosmetic products.
- Limitations : Less specific than HPLC, this method is used mainly for routine controls.
Importance of compliance analyses
ISO standards and COFRAC certifications
- Analyses must be carried out in laboratories accredited according to ISO 17025 to guarantee their reliability and traceability.
- The certifications ensure that the results comply with current regulatory requirements, particularly in the areas of food and cosmetic safety.
Purity and identification tests
- Detection of contaminants or impurities in glycyrrhizic acid extracts, including pesticides or heavy metals.
- Validation of chemical identity to prevent substitutions or counterfeits.
Stability studies
- Evaluation of the stability of glycyrrhizic acid in different formulations, taking into account factors such as temperature, light or pH.
- These analyses are essential to guarantee the lifespan and effectiveness of products containing this ingredient.
Concrete examples of analyses
Dietary supplements
- Matrix: Capsules or powders based on licorice.
- Method: HPLC-UV.
- Detection limit: 10 ppm.
Cosmetics
- Matrix: Lightening serums or creams.
- Method: Mass spectrometry to detect very low concentrations.
Medicinal plants
- Matrix: Roots or extracts of licorice.
- Method: Extraction followed by HPLC to quantify glycyrrhizic acid.
5. Applications and uses of glycyrrhizic acid
Food and beverage applications
Natural sweetener
- Glycyrrhizic acid is used as a natural sweetener, particularly in soft drinks, chewing gum, and licorice-based candies.
- Advantages : Its sweetening power is 30 to 50 times greater than that of sucrose, with a prolonged sweet sensation and a low caloric contribution.
- Regulation : Identified under the number E958, it is authorized as a food additive in several countries, although limits are imposed on its consumption to avoid side effects such as hypertension.
Flavor enhancer
- Used to mask the bitterness of artificial sweeteners like saccharin and acesulfame K, or to enhance the taste in complex formulations.
Dietary supplements
- Used for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, particularly in health and wellness products.
Cosmetic applications
Soothing and brightening agent
- Glycyrrhizic acid is a key ingredient in skincare for calming irritations, reducing redness and evening out skin tone.
- Products concerned : Serums, moisturizing creams, after-sun care, and treatments for sensitive skin or skin prone to hyperpigmentation.
Anti-aging protection
- By inhibiting certain enzymes such as matrix metalloproteinases, it slows down skin aging by preventing the degradation of collagen and elastin.
Specific applications
- Oral hygiene : Incorporated into toothpastes for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties.
- Sunscreen products : Used in sunscreen formulations to mitigate UV damage and protect skin cell DNA.
Pharmaceutical applications
- Anti-inflammatory
- Used in creams and ointments to relieve skin irritations such as diaper rash or sunburn.
- Antiviral and protective properties
- Studies have shown that glycyrrhizic acid inhibits certain viruses, including those responsible for hepatitis and herpes.
- Sore throat medications
- Available in lozenges or sprays to soothe inflammation and pain.
Other industrial uses
Tobacco industry: Glycyrrhizic acid is used as an additive to enhance the flavor of tobacco products. Although controversial, this practice remains common in some countries.
Biopolymer manufacturing: Used for its bioactive properties in the development of biodegradable materials, particularly in food packaging.
Chemical precursor: Used in the synthesis of pharmaceutical and cosmetic compounds, notably for the manufacture of glycyrrhetinic acid, a derivative with high therapeutic potential.

6. Regulations and precautions related to glycyrrhizic acid
Food consumption limits
Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI): In Europe, glycyrrhizic acid consumption is limited to 100 mg per day , as recommended by the Scientific Committee on Food (SCF). This limit was set to prevent side effects associated with excessive consumption, such as hypertension and electrolyte imbalances.
Mandatory labeling on products: Since a 2004 European directive, food products containing glycyrrhizic acid or its salts must indicate the presence of licorice if their concentration exceeds a certain threshold. This includes statements such as:
- "Contains licorice – people with high blood pressure should avoid excessive consumption."
Regulations in cosmetics
European standards
- Glycyrrhizic acid is permitted in cosmetic products without specific concentration restrictions, although its derivative, glycyrrhetinic acid, is more common.
No major restrictions
- Studies demonstrating that glycyrrhizic acid is neither irritating nor sensitizing at concentrations up to 6% have led to a lack of strict limits in European cosmetic regulations.
Risks associated with excessive consumption
Health effects: Excessive consumption (> 1 g/day) may lead to side effects, including:
- Arterial hypertension : Due to inhibition of the 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase enzyme, causing an accumulation of cortisol.
- Hypokalemia : Resulting from excessive potassium loss, which can cause heart and muscle problems.
- Water retention : Can lead to edema and an increase in blood volume.
Overdose cases: Incidents have been reported in people regularly consuming large quantities of licorice or glycyrrhizin-based products, sometimes requiring hospitalization.
Recommendations for safe use
Sensitive populations: People suffering from hypertension, heart disease, or kidney disorders should limit their exposure to glycyrrhizic acid.
Controlled use in food and cosmetic products: Manufacturers must ensure compliance with dosage recommendations and inform consumers of potential risks.
Ongoing regulatory monitoring: Studies are underway to assess safe exposure levels and adapt recommendations accordingly.
International regulations
United States: Glycyrrhizic acid is considered "GRAS" (Generally Recognized as Safe) by the FDA, but its use as a food additive is restricted in some states.
Japan: Strict limit of 200 mg/day to ensure safe use. Glycyrrhizic acid is often combined with other natural sweeteners to reduce its concentration.
France: In addition to European directives, France requires a specific statement on products containing licorice in order to raise consumer awareness of potential risks.




