Acetic anhydride , also known as ethanoic anhydride , is a chemical compound widely used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
It plays a key role in many industrial processes, particularly as an acetylation and dehydration agent. While highly useful, it requires careful handling due to its toxicity and flammability. This compound also finds specific applications in the food industry , notably for the production of additives and preservatives. This first part explores in detail the fundamental properties of acetic anhydride, providing a clear understanding of this essential compound.
1. What is acetic anhydride?
Chemical definition
Acetic anhydride, with the chemical formula C4H6O3 , is the product of the condensation of two acetic acid molecules with the elimination of one water molecule. This dehydration process results in a symmetrical molecule composed of two acetyl groups linked by an oxygen atom.
Synonyms for acetic anhydride include:
- Ethanoic anhydride
- Acetic anhydride (English name)
- Acetyl oxide or ethanolic anhydride
These names are often used in scientific literature and technical data sheets, reflecting the versatility of this compound in various applications.
Physical and chemical properties
The properties of acetic anhydride give it unique characteristics that make it useful in many chemical syntheses. Here is a summary of its main properties:
- Molar mass : 102.09 g/mol
- Density : 1.08 g/cm³ (at 20 °C)
- Boiling point : 139 °C
- Melting point : -73 °C
- Solubility : Although it is slightly soluble in water (approximately 120 g/L at 20 °C), acetic anhydride dissolves readily in organic solvents such as ethanol, acetone, or chloroform.
Upon contact with water or atmospheric moisture, acetic anhydride hydrolyzes rapidly, releasing acetic acid. This exothermic reaction requires precautions during handling, as it can generate fumes that are irritating to the eyes and respiratory tract.
Chemical reactivity
Acetic anhydride is highly reactive due to its acetyl groups. It is commonly used as an acetylation agent, that is, to introduce acetyl groups into target molecules. This property is exploited in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and even some dyes.
In summary, acetic anhydride is an essential chemical compound in many industries due to its unique properties. However, its handling requires a thorough understanding of its physical and chemical characteristics to ensure safe and effective use.

2. How to produce acetic anhydride in the laboratory
Acetic anhydride can be synthesized in the laboratory and on an industrial scale using several methods. Each method relies on specific chemical reactions and optimized conditions to ensure efficient production. This section explores the main techniques for manufacturing acetic anhydride, highlighting the essential reactions and parameters.
Synthesis via ketone
The ketone-based method is a commonly used approach in laboratories. It involves two main steps:
Formation of ketene : CH3COOH 700 °C, under vacuum CH2=C=O+H2O
Acetic acid is heated to a high temperature (700 °C) under vacuum, causing its decomposition into ketene (CH2=C=O) and water:
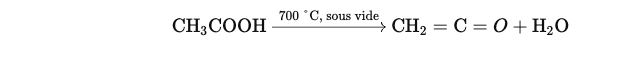
This reaction is often catalyzed by esters of phosphoric acid, such as triethyl phosphate.
- Reaction of ketone with acetic acid :
The ketene obtained then reacts with another molecule of acetic acid to form acetic anhydride:
CH2=C=O+CH3COOH→(CH3CO)2O
This step is quick and efficient, and it allows for the production of acetic anhydride with a high yield.
Eastman Process
The Eastman process is a key industrial method based on the carbonylation of methyl acetate. This method relies on a reaction catalyzed by rhodium and other specific co-catalysts. The main steps are as follows:
Initial reaction : CH3COOCH3+CO→(CH3CO)2O
Methyl acetate (CH3COOCH3) is subjected to carbon monoxide (CO) pressure in the presence of a rhodium-based catalyst:
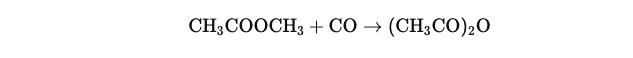
This reaction is carried out under controlled temperature and pressure conditions, generally between 150 and 200 °C and at a pressure of 20 to 40 bars.
- Advantages of the process :
- Enables large-scale production.
- Effective for achieving high yields with precise control of by-products.
BP Chemicals Process
This method, similar to the Eastman process, also relies on the insertion of carbon monoxide into methyl acetate. However, it uses a quaternary ammonium salt as a co-catalyst to improve reaction efficiency. The BP Chemicals process produces a mixture of acetic acid and acetic anhydride, which is often subsequently separated to meet specific industry requirements.
Comparison of methods
| Method | Benefits | Disadvantages |
| Synthesis via ketone | Suitable for laboratories, high yield | Extreme temperature conditions, high costs |
| Eastman Process | Efficient industrial production | Requires specialized equipment |
| BP Chemicals Process | Optimized catalysis for high yields | Produces a mixture requiring separation |
In conclusion, the manufacture of acetic anhydride depends on specific needs and available resources. Laboratory methods, such as synthesis via ketene, are suitable for small quantities, while industrial processes, such as the Eastman and BP Chemicals methods, are designed for large-scale production.
Are you looking for an analysis?

3. Applications of acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride is a versatile chemical compound widely used in various industrial sectors. Thanks to its unique chemical properties, it plays a central role in complex organic syntheses and large-scale industrial processes. This section explores the different applications of acetic anhydride and highlights its importance in several key industries.
Use in organic chemistry
Acetic anhydride is primarily used as an acetylation agent, a chemical reaction in which an acetyl group is introduced into a target molecule. This process is essential for the chemical modification of many substances.
- Aspirin synthesis : Acetic anhydride is a key ingredient in the manufacture of acetylsalicylic acid, better known as aspirin. The acetylation reaction of salicylic acid using acetic anhydride is rapid, efficient, and generates few byproducts.
- Paracetamol synthesis :
The acylation of p-aminophenol with acetic anhydride produces paracetamol, another commonly used medication. This reaction ensures high purity and economical production. - Cellulose acetate production:
Acetic anhydride reacts with cellulose to produce cellulose acetate, a polymer used in the manufacture of photographic films, textiles, and biodegradable plastics.
Applications in industrial sectors
Acetic anhydride also finds applications in several industries, where it is used to modify or improve the properties of various products.
- Food industry :
- It is used for the modification of food starches, allowing for improvements in their stability, texture, and functional properties.
- These modified starches are often used as thickeners in sauces, desserts, or processed products.
- Pharmaceutical and cosmetics industry :
- In pharmaceuticals, it is used to manufacture drugs from chemical precursors.
- In cosmetics, it is used to stabilize certain formulations and to improve the texture of products.
- Manufacturing of plastics and dyes :
- Acetic anhydride is used to produce durable plastics, including those based on acetate.
- It also participates in the synthesis of pigments and dyes for textiles and various materials.
- Production of explosives and perfumes :
- It is used in the manufacture of certain specific explosives, where it acts as a chemical reagent.
- In perfumery, it is used to synthesize complex aromatic compounds.
Regulation and control of use
Because of its role in the synthesis of controlled substances, such as heroin (via the diacetylation of morphine), acetic anhydride is classified as a controlled chemical precursor. In many countries, its use and distribution are strictly regulated.
- International regulations :
- In the United States, it is listed on DEA Schedule II, which groups together controlled chemical precursors.
- In the European Union, its use is regulated by strict laws concerning hazardous substances.
- Traceability and mandatory reporting :
- Any handling of large quantities of acetic anhydride must be reported to the competent authorities.
- Companies using this compound must ensure rigorous controls to prevent any diversion.
In summary, acetic anhydride is an essential ingredient in many industries, playing a crucial role in the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and other products. However, its use must be strictly controlled to prevent the risks of diversion or misuse.

4. Analytical properties and laboratory analyses
Acetic anhydride is a compound widely studied in the laboratory due to its industrial applications and potential environmental impact. This section explores the main techniques used for its analysis, compliance standards, and the importance of laboratory testing to ensure its safety and quality.
Analytical methods used for acetic anhydride
Gas chromatography (GC) :
Gas chromatography is one of the most widely used techniques for detecting and quantifying acetic anhydride in various samples. It can be coupled with different types of detectors:
- GC-FID (Flame Ionization Detector) : Allows detection of organic compounds with high sensitivity.
- GC-NPD (Nitrogen-Phosphorus Detector) : Particularly suitable for compounds containing nitrogen or phosphorus, such as in complex samples.
Acid-base titration :
Although less specific, titration is a traditional method still used to measure the concentration of acetic anhydride in aqueous mixtures. In a basic medium, acetic anhydride is hydrolyzed to acetic acid, which allows its quantity to be determined as a function of pH.
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy :
This technique makes it possible to identify the characteristic functional groups of acetic anhydride through specific peaks in the IR spectrum, particularly those linked to C=O bonds (carbonyl groups).
Importance of analyses that comply with standards
ISO 17025 and COFRAC certifications :
Laboratories performing acetic anhydride analyses must be certified according to ISO 17025 standards, guaranteeing the reliability and reproducibility of results. In France, COFRAC accreditation reinforces laboratories' compliance with European standards.
Specific regulations :
The tests carried out must comply with current regulations, such as those relating to hazardous substances or chemical precursors.
Applications of laboratory analysis
Quality control :
The analyses guarantee the purity of the acetic anhydride, which is crucial in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
Contaminant detection :
Particularly in food or pharmaceutical products, laboratories check for the presence of potentially toxic by-products or residues.
Environmental monitoring :
The laboratories also carry out analyses to monitor the presence of acetic anhydride in industrial effluents, thus ensuring compliance with environmental standards.
Scientific analysis inspired by methods used on malic acid
Analytical methods for acetic anhydride
Acetic anhydride analysis relies on advanced techniques to ensure accurate detection and quantification. Common methods include:
Chromatography :
- High-performance liquid chromatography ( HPLC ) is used in some cases to detect traces of acetic anhydride in complex matrices.
- However, GC, mentioned previously, remains the preferred method.
Chemical titration :
As with malic acid , an acid-base titration can be used to measure the concentration of acetic anhedride, although this method lacks precision for complex samples.
Compliance and safety testing
Compliance with international standards :
The analyses must meet the requirements of ISO 17025 standards and European and American regulations, such as EC Regulation No. 1935/2004 for materials in contact with food.
Industrial product monitoring :
Regular testing is necessary to ensure that products containing acetic anhydride meet regulatory thresholds and pose no risk to consumers or the environment.
Impact on industrial formulations
Acetic anhydride can influence the stability and quality of the formulations in which it is used. For example:
- In food products : It is essential to control its interaction with other components to avoid adverse reactions.
- In plastics and cosmetics : Laboratories evaluate its impact on the texture, stability and overall performance of finished products.
In summary, laboratory analyses play a crucial role in ensuring that acetic anhydride is used safely and in accordance with regulations. These tests also help optimize industrial processes and guarantee the quality of finished products.

5. Why is acetic anhydride used?
Acetic anhydride is a key chemical reagent due to its unique properties, which make it a versatile tool in many industries. This section explores the main reasons for its common use and the advantages it offers in different contexts.
Advantages in chemical synthesis
Efficacy in acetylation reactions :
Acetic anhydride is primarily used as an acetylation agent, allowing the introduction of acetyl groups into target molecules. This chemical transformation is rapid and efficient, generating high yields with minimal byproducts.
Example: The synthesis of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) relies on this acetylation capacity.
Dehydration reactions :
Acetic anhydride is also used to remove water from chemical compounds, facilitating the formation of esters, amides, and other organic compounds. This property is essential in the production of polymers and complex chemicals.
Use in industrial applications
- Pharmaceutical industry :
- Acetic anhydride is essential in the manufacture of medicines such as aspirin and paracetamol.
- It is also used to synthesize chemical precursors needed for the production of complex drugs.
- Food industry :
- In this sector, it is used to modify food starches, improving their stability, viscosity, and ability to be incorporated into various formulations. These modified starches are often found in sauces, soups, and processed desserts.
- As an authorized food additive, it ensures the functionality of products without altering their taste or texture.
- Plastics and Polymers Industry :
- Cellulose acetate, produced using acetic anhydride, is used in the manufacture of biodegradable plastics, transparent films, and textiles.
- These applications highlight its role in the development of environmentally friendly materials.
- Cosmetics industry :
- Acetic anhydride is used to stabilize certain cosmetic formulations and improve their texture. It also plays a role in the synthesis of active ingredients for creams and lotions.
- Perfumery and aromas :
- In perfumery, it is used to manufacture complex aromatic esters, which serve as bases for sophisticated fragrances.
- Food flavorings also benefit from the use of acetic anhydride to create specific flavors.
Technical and economic advantages
Economic production :
Industrial processes, such as those of Eastman and BP Chemicals, make it possible to produce acetic anhydride on a large scale and at competitive costs, making its use accessible to a wide range of industries.
Chemical versatility :
- Its use is not limited to a single sector, making it a versatile product.
- Its reactive properties apply to a wide range of reactions, from basic organic chemistry to the production of advanced polymers.
Limited environmental impact :
Although acetic anhydride is a reactive substance, its rapid hydrolysis in water limits its environmental impact, making it a relatively safe choice for industrial processes when handled correctly.
In summary, acetic anhydride is an indispensable component in numerous applications due to its reactivity, versatility, and accessibility. Whether in chemical synthesis, the food industry, or cosmetics, its use continues to play a central role in the innovation and efficiency of industrial processes.




