Acetic acid, also known as ethanoic acid, is an essential organic compound in many industries, including food processing , chemicals, and pharmaceuticals. Known as the main component of vinegar, it also plays a fundamental role in the manufacture of numerous industrial and pharmaceutical products. This colorless liquid, with its characteristic taste and odor, is commonly used as a solvent, chemical reagent, and food additive. This article explores in detail the properties, production, and applications of acetic acid, highlighting its importance and laboratory analysis methods.
YesWeLab offers you a full range of laboratory analysis services, combining expertise and cutting-edge technologies to guarantee the quality and compliance of your products.
Table of Contents
What is acetic acid?
Definition and chemical formula
Physicochemical properties
Acetic acid is a carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C₂H₄O₂ , often represented in its expanded form CH₃COOH -COOH functional group gives it its characteristic acidity. It belongs to the family of monocarboxylic acids and is classified as a weak acid in aqueous solution. It should not be confused with peracetic acid (C₂H₄O₃), a powerful oxidizing agent used as a disinfectant and sterilizer, whose chemical properties and applications differ from those of acetic acid.
Acetic acid can exist in different forms:
- Glacial acetic acid 99.5% pure form , which solidifies below 16.6 °C . It is so named because of its crystalline appearance when it freezes.
- Aqueous solutions : Depending on the concentration, it is used as an acidity regulator in the food industry.
In aqueous media, acetic acid partially dissociates into acetate ions (CH₃COO⁻) and hydronium ions (H₃O⁺) , which explains its moderate acidity with a pKa of 4.76 . This characteristic differentiates it from strong acids such as sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid.
Acetic acid has specific properties that explain its use in many industrial and scientific fields.
- Melting and boiling points :
- Melting point: 16.6 °C
- Boiling point: 117.9 °C
- Density : 1.05 g/cm³ at 20 °C
- Solubility : Completely miscible with water, ethanol, diethyl ether and other organic solvents.
- Acidity : pKa = 4.76 , characteristic of a weak acid.
- Flammability : Flash point at 40°C , which makes it flammable under certain conditions.
- Corrosivity : Can attack certain metals such as zinc and iron, forming metallic acetates and releasing dihydrogen.
Acetic acid forms molecular dimers in the gas phase and in non-aqueous solution. These structures are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl groups of the molecules, which modifies some of its physicochemical properties.
History and Discovery
The use of acetic acid dates back to antiquity, where it was mainly consumed in the form of vinegar . The first mentions of its production date back several millennia, with the natural fermentation of alcoholic beverages left in the open air.
- Antiquity :
- The Egyptians and Babylonians used vinegar for food preservation.
- Theophrastus, a Greek philosopher of the 3rd century BC, describes the effect of vinegar on metals and its transformation into acetate salts.
- Middle Ages and Renaissance :
- Alchemists improved the distillation of vinegar to obtain higher concentrations of acetic acid.
- Glacial acetic acid is produced by dry distillation of metallic acetates (notably lead acetate).
- 19th and 20th centuries :
- In 1847 , Hermann Kolbe succeeded in synthesizing acetic acid from inorganic compounds, paving the way for industrial production.
- Around 1910 , the production of acetic acid was mainly based on the distillation of wood (pyroligneous liquor).
- Around 1910 , the production of acetic acid was mainly based on the distillation of wood (pyroligneous liquor).
Today, more than 6.5 million tons of acetic acid are produced annually worldwide, with increasing demand in the chemical, pharmaceutical and food sectors.

Production and synthesis of acetic acid
Acetic acid is produced on an industrial scale using various processes, allowing for purity levels suited to the needs of different applications. Although production by bacterial fermentation is historically the oldest method, it is now marginal, having been superseded by modern chemical that are more efficient and better suited to industrial requirements.
Industrial manufacturing methods
Methanol carbonylation: dominant process
The most common method used for the industrial production of acetic acid is the carbonylation of methanol , which accounts for approximately 75% of world production . This process is based on the reaction of methanol ( CH₃OH ) with carbon monoxide (CO) under homogeneous catalysis.
Chemical reaction :
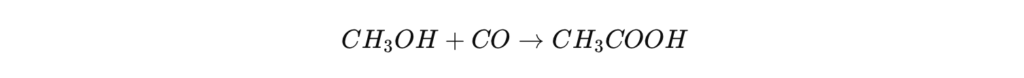
The Monsanto process , developed in the 1970s by Monsanto, uses rhodium (Rh) as its main catalyst. It was replaced in the 1990s by the Cativa process , developed by BP Chemicals , which uses an iridium (Ir) that is more efficient and generates fewer undesirable byproducts.
Advantages of methanol carbonylation:
- High yield (greater than 95 %).
- Less waste and polluting by-products.
- Reduced production costs thanks to optimized catalysts.
Oxidation of acetaldehyde
Before the widespread adoption of the Monsanto process, the main method of producing acetic acid was based on the oxidation of acetaldehyde (CH₃CHO) using oxygen from the air under the effect of a metallic catalyst (manganese, cobalt or chromium).
Chemical reaction :
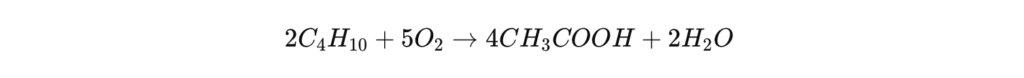
Although still used, this method is now in the minority due to its yield of less than 85% and the presence of secondary by-products such as formic acid and ethyl acetate .
Oxidation of butane and ethylene
Another industrial alternative is to oxidize butane (C₄H₁₀) or ethylene (C₂H₄) in liquid phase , in the presence of a metallic catalyst.
Chemical reaction for butane :
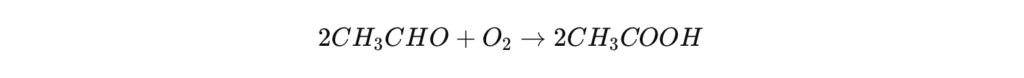
This process, used by some industries, makes it possible to obtain high-purity acetic acid , but it is less profitable than the carbonylation of methanol, due to its higher energy cost.
Bacterial fermentation: a natural process
The production of acetic acid by bacterial fermentation vinegar production , particularly for food applications. This process relies on the action of acetic bacteria of the genus Acetobacter , which transform ethanol (C₂H₅OH) into acetic acid in the presence of oxygen.
Biological reaction :
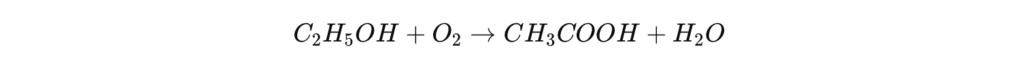
This process is not very efficient for large-scale industrial production, but it remains essential for the production of vinegar , because regulations require that vinegar intended for human consumption be produced by a biological process .
Major producers and the global market
Global production and geographical distribution
Global acetic acid production is estimated at around 6.5 million tonnes per year . It is concentrated in a few industrialized countries with large petrochemical capacities .
- United States : world's leading producer, with an annual capacity exceeding 2.5 million tons .
- China : production is growing rapidly, particularly thanks to investments in petrochemicals.
- Europe : production is declining, with a capacity of approximately 1 million tonnes per year .
- Japan : historical player in the market, producing approximately 0.7 million tonnes .
Major players in the industry
A few companies dominate global acetic acid production, including:
- Celanese (United States)
- BP Chemicals (United Kingdom)
- Eastman Chemical Company (United States)
- LyondellBasell (Netherlands)
- Daicel (Japan)
These companies control global production and supply, directly influencing the prices and availability of acetic acid on the market.
Economic and environmental challenges
Acetic acid is a key intermediate in the chemical industry, used in the manufacture of plastics, solvents, and pharmaceuticals . However, its environmental impact is monitored due to the production of CO₂ and volatile compounds during certain processes.
Current challenges in the sector include:
- Optimizing processes to limit greenhouse gas emissions.
- Recycling of secondary waste streams to reduce industrial waste.
- Development of more efficient catalysts to increase yields and limit by-products.
Evolving international regulations require manufacturers to reduce the environmental impact of chemical processes, which could encourage the development of new, more environmentally friendly production techniques .
Are you looking for an analysis?

Uses and applications of acetic acid
Acetic acid is a versatile compound used in many industrial sectors. Its role extends from the chemical industry to food processing, including pharmaceuticals, plastics, and textiles. Thanks to its acidic and solvent properties, it is used in the manufacture of products as varied as polymers, solvents, food additives, and pharmaceuticals.
Chemical and pharmaceutical industry
Production of acetic anhydride and acetates
Acetic acid is an essential precursor in the production of acetic anhydride (C₄H₆O₃) , a reactive substance used in the synthesis of many organic compounds. It is primarily used for:
- The manufacture of cellulose acetate , used in the production of plastic films, synthetic textiles and cigarette filters.
- The synthesis of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) , which is based on a reaction between acetic anhydride and salicylic acid .
Acetic anhydride is also used in the manufacture of heroin , making it a product strictly controlled by regulatory authorities.
Production of solvents and plastics
Acetic acid is a key intermediate in the manufacture of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) , an essential compound for the production of polymers and resins. It is used in the manufacture of:
- Paints and adhesives , via polyvinyl acetate (PVA).
- Plastic films and textile fibers , by the polymerization of vinyl acetate.
Other industrial solvents , such as ethyl acetate and butyl acetate, are produced from acetic acid and are used in the paints, varnishes and printing inks industry.
Pharmaceutical and disinfectant use
Acetic acid is used in the pharmaceutical industry for its antiseptic and bacteriostatic properties . It is notably used for:
- Disinfect wounds and medical surfaces using diluted solutions.
- Treating certain bacterial infections in dermatology and otorhinolaryngology.
- To serve as an excipient in pharmaceutical formulations , as a pH adjuster.
Agri-food: role and regulations
Acetic acid as a food additive (E260)
Acetic acid is an acidity regulator widely used in the food industry under the code E260 . It is present in:
- Food vinegars , of which it is the main active constituent.
- Sauces, marinades and condiments , where it enhances flavor and preservation.
- Bakery products , to control acidity and fermentation.
The European Union and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorize the use of acetic acid in food under certain strict concentration limits.
Vinegar production by fermentation
Vinegar is an aqueous solution of acetic acid obtained by the biological fermentation of ethanol in the presence of bacteria of the genus Acetobacter . This natural process has been used for millennia for food preservation.
Types of vinegar according to their origin:
- Wine vinegar : produced from the fermentation of red or white wine.
- Apple cider vinegar : produced from fermented apples.
- Balsamic vinegar : made from concentrated grape must and aged in wooden barrels.
Food-grade vinegar must contain at least 4% acetic acid to be marketed in Europe.
Food regulations and safety
The use of acetic acid in the food industry is strictly regulated to ensure consumer safety . The main regulatory frameworks are:
- European Union Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008
- The purity standards imposed by the Codex Alimentarius .
- Migration controls in food packaging, in accordance with EC Regulation No. 1935/2004 .
Other industrial applications
Textile and tannery industry
Acetic acid is used in the textile industry for:
- Fixing dyes onto natural and synthetic fibers , by adjusting the pH of the dye baths.
- Improve the durability of prints on fabrics , especially for cotton and polyester textiles.
In tanneries , it is used for the pretreatment of hides (prickling) before tanning, adjusting their pH to optimize the absorption of tanning agents.
Photography and electronics
photographic development processes , acetic acid is used in the form of a stop bath to interrupt the action of the developer and fix the image.
In the electronics industry, it is used as a cleaning agent in the manufacture of semiconductors , particularly to remove metallic residues and adjust the surfaces of electronic components.
Cleaning and disinfection
Diluted acetic acid is an descaling and cleaning for:
- Eliminating limescale and tartar deposits in industrial machines and installations.
- Disinfecting surfaces and equipment in the agri-food and medical sectors.
Its action against bacteria and mold makes it a key ingredient in some eco-friendly cleaning products , particularly multi-purpose cleaners based on vinegar.
Acetic acid therefore plays an essential role in many industrial applications, due to its specific chemical properties and its wide availability on the global market.

Laboratory analyses on acetic acid
Acetic acid is widely used in industry, necessitating rigorous analysis to ensure its purity, regulatory compliance, and safety in various applications. Specialized laboratories conduct tests to verify acetic acid concentration, detect impurities, and ensure that products containing this substance meet regulatory requirements.
Importance of analyses and regulatory issues
Laboratory tests are essential for:
- To guarantee the quality and purity of acetic acid used in the chemical, pharmaceutical and food industries.
- Verify regulatory compliance ISO 17025 standards COFRAC accreditations .
- Detect impurities and contaminants , including traces of heavy metals, residual solvents and synthetic by-products.
- Evaluate the concentration of acetic acid in various products, such as vinegar, solvents, and industrial solutions.
In the food and pharmaceutical production sectors, laboratories must comply with strict regulations, including:
- Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 on food additives.
- Regulation (EC) No 1935/2004 on materials in contact with food.
- European pharmacopoeia standards for pharmaceutical products.
Analytical techniques used
Various analytical methods allow the concentration of acetic acid to be measured and its impurities to be identified in various matrices.
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
HPLC is a commonly used technique for analyzing acetic acid in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical products. It allows for :
- To accurately quantify the acetic acid content.
- Separate and identify the impurities present in a sample.
- Verify that the product complies with applicable standards.
It is particularly used for quality control of vinegar , where it allows the exact concentration of acetic acid to be determined and ensures that it complies with regulations.
Ion chromatography
Ion chromatography is used to detect and measure volatile acids , including acetic acid, in air, water, and materials . This technique is essential for:
- Controlling industrial and environmental pollution.
- Check the concentration of acetic acid in solvents and aqueous solutions.
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
Acid-base titration
Acid-base titration is a classic method for measuring the concentration of acetic acid in a solution. It relies on neutralizing the acid with a strong base (NaOH), using a pH indicator. This technique is:
- Simple and quick , suitable for routine analyses.
- Precise for aqueous solutions , such as vinegars or dilute acetic acid solutions.
Gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS)
GC -MS is used for the analysis of acetic acid in water and complex matrices . This method is essential for:
- Detect the presence of acetic acid in volatile mixtures.
- Identify the contaminants associated with its production.
Migration tests for food contact materials
Since acetic acid is a pH regulating agent , it is often used in food packaging to test the migration of chemical substances .
Regulations and the importance of migration testing
Plastic packaging, paper, inks and varnishes must comply with EC Regulation No. 1935/2004 , which imposes strict limits on the migration of chemical compounds into food.
Migration tests performed in the laboratory allow us to:
- Evaluate the interaction between the packaging and foods containing acetic acid.
- Check that the materials do not release toxic substances under the effect of acidity.
- Ensure packaging complies with European and American (FDA) standards.
Laboratory testing methods
The laboratories simulate real-world usage conditions by exposing the packaging to a 3% or 10% , then measuring the migration of substances using:
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to detect contaminants.
- Mass spectrometry (GC-MS or ICP-MS) for the identification of migrated compounds.
Rheological analyses and their impact on formulations
Acetic acid influences the texture and stability of industrial formulations, particularly in food and cosmetic products.
Study of viscosity and fluidity
Laboratories perform rheological tests to analyze:
- The fluidity and texture of sauces, creams and food products , where acetic acid can play a stabilizing role.
- The viscosity of pharmaceutical and cosmetic solutions , where it plays a role in pH regulation.
These analyses are carried out using rheometers , allowing the product's response to mechanical stress to be measured.
Stability and compatibility of formulations
Adding acetic acid to a formulation can affect:
- The stability of emulsions and creams , requiring pH adjustment.
- Interaction with other ingredients , particularly polymers and thickening agents.
Laboratory tests allow for the optimization of formulations to ensure better preservation and optimal product performance .
Laboratory analysis of acetic acid is therefore essential to ensure its quality, regulatory compliance and integration into various industrial applications .
Risks and precautions related to acetic acid
Acetic acid, although used in numerous industrial and food applications, presents certain risks to health and the environment . It is important to understand its effects, hazards, and the precautions necessary for safe handling.
Toxicity and health effects
Acetic acid can have harmful effects depending on its concentration and mode of exposure.
Inhalation exposure
Acetic acid fumes are irritating to the respiratory tract and can cause:
- Coughs and irritations resulting from prolonged exposure.
- A burning sensation in the nose and throat , even at low concentrations.
- Pulmonary edema can occur in cases of exposure to high concentrations (greater than 25 ppm).
Contact with skin and eyes
Acetic acid is corrosive at high concentrations and can cause:
- skin burns can occur upon contact with glacial acetic acid.
- Severe eye irritation , which can cause chemical conjunctivitis.
- Irreversible tissue damage can occur in cases of prolonged exposure to concentrated solutions.
Effects of accidental ingestion
Ingesting highly concentrated can be very dangerous:
- Heartburn and stomach irritation.
- Abdominal pain and vomiting.
- Risk of gastric perforation in case of exposure to high concentrations.
Diluted solutions, such as food-grade vinegar, do not present a significant health risk at usual consumption doses.
Regulations on occupational exposure
Acetic acid is subject to exposure limits in the workplace to protect workers.
Exposure limit values (ELVs)
Regulations set exposure limit values to avoid health risks:
- VLE in France (INRS) :
- 10 ppm (25 mg/m³) over 8 hours.
- 15 ppm (37 mg/m³) in short exposure (15 minutes).
- OSHA (United States) standards : 10 ppm over 8 hours .
Hazard classification according to CLP regulations
Acetic acid is classified as a hazardous substance according to EC Regulation No. 1272/2008 (CLP) :
- H226 : Flammable liquid and vapor.
- H314 : Causes severe skin burns and eye damage.
- H335 : May cause respiratory irritation.
Companies handling acetic acid must implement preventative measures to avoid any dangerous exposure.
Safety measures and storage
Safe handling of acetic acid is essential to reduce the risk of accidents.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Exposed workers must wear:
- Chemical-resistant gloves , made of nitrile or neoprene.
- Protective glasses or a face shield.
- A mask with a filter suitable for acid vapors , in case of prolonged use.
- A protective suit , to avoid any contact with the skin.
Storage conditions
Acetic acid must be stored carefully to avoid the risk of fire and chemical reaction.
- Store in a cool, ventilated place , away from heat sources.
- Use corrosion-resistant containers , such as stainless steel or high-density plastic.
- Avoid contact with strong bases, powerful oxidants, or reactive metals , which could cause dangerous reactions.
Procedures in case of leak or accident
In case of accidental spillage, it is recommended to:
- Evacuate the area and limit exposure to the fumes.
- Neutralize the leak with sodium bicarbonate before cleaning.
- Dispose of waste in accordance with environmental regulations.
Environmental impact and waste disposal
Acetic acid, although biodegradable, can have an environmental impact if released in large quantities.
Effects on the environment
- Water contamination : excessive discharge can acidify aquatic environments , endangering fauna and flora.
- Atmospheric emissions : vapors can contribute to air irritation in urban or industrial environments.
Industrial waste disposal
Companies using acetic acid must follow strict protocols for waste disposal:
- Neutralization before discharge : it is often neutralized with a base such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) before being discharged into wastewater.
- Treatment by controlled incineration to avoid dispersion into the environment.
- Compliance with European and local standards for the treatment of chemical waste.
Acetic acid, although commonly used, therefore requires rigorous handling , appropriate safety protocols and controlled waste management to limit its risks to health and the environment.
YesWeLab: Analytical solutions for acetic acid
Acetic acid analysis is essential to ensure the quality, regulatory compliance, and safety of products containing it. YesWeLab, through its network of over 200 partner laboratories , offers analytical solutions tailored to the needs of manufacturers in various sectors.
Why analyze acetic acid with YesWeLab?
Manufacturers using acetic acid in their formulations must perform accurate analyses that comply with current standards . YesWeLab offers analytical services that enable:
- Control the purity and concentration of acetic acid in raw materials and finished products.
- Detect impurities and contaminants , such as residual solvents or heavy metals.
- Ensure the safety of consumers and workers by assessing the potential risks associated with its use.
Thanks to its expertise, YesWeLab supports companies in their certification and validation processes for products containing acetic acid.
Analysis process with YesWeLab
YesWeLab facilitates access to laboratory analyses through a simplified and digitalized process .
Manufacturers can find the analyses suited to their needs by consulting the online catalogue of YesWeLab, which offers more than 10,000 analytical services .
Among the analyses available for acetic acid:
- Determination of acetic acid in solvents, food and pharmaceutical products.
- Search for impurities and residual solvents.
- Migration tests for packaging in contact with acidic products.
- Stability and compatibility analyses of formulations.
Laboratory analysis
The samples are handled by laboratories equipped with the latest analytical technologies:
- High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
- Ion chromatography.
- FTIR spectroscopy.
- Acid-base titration.
- GC-MS for complex solvents and matrices.
Specific tests for materials in contact with acetic acid
YesWeLab offers migration testing to ensure that packaging and materials comply with applicable standards. These tests are particularly important for:
- Food packaging , in order to avoid contamination of acidic products.
- Industrial coatings and plastics , to guarantee their resistance to acidity.
- Production equipment , in order to prevent corrosion and wear of materials.
Acetic acid is widely used in many sectors, making it essential to guarantee its quality and compliance through rigorous analysis. By partnering with YesWeLab, manufacturers benefit from a comprehensive, digital service that allows them to optimize their formulations and ensure product safety.




