Accelerated aging testing is a laboratory simulation method used to predict how a material or product will behave over time by subjecting it to controlled, extreme conditions. This process evaluates resistance to heat, humidity, UV radiation, mechanical stress, and chemical agents to detect potential performance degradation.
Among the commonly used tests, salt spray testing is used to assess the corrosion of metallic materials, while the Rancimat method is essential for determining the oxidative stability of fatty or oily products . These tools are fully integrated into a product validation strategy, regardless of the industrial sector involved: polymers, cosmetics, medical devices, or food processing.
By rapidly reproducing the effects of aging, these tests allow manufacturers to predict product lifespan, optimize formulations, and ensure regulatory compliance. YesWeLab supports manufacturers with a wide range of specialized analyses to assess the durability, stability, and reliability of their materials.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Definition of the accelerated aging test
Accelerated aging testing is an experimental method that involves exposing a material or product to extreme environmental conditions to observe its evolution over a short period. Rather than waiting several years to observe the wear and tear of a product in its natural environment, laboratories reproduce these conditions by amplifying them, thus simulating the equivalent of several years of aging in a few weeks or months .
The parameters typically applied in these tests include:
- High temperature to accelerate chemical and physical reactions.
- Controlled humidity to simulate exposure to water and climatic variations.
- Exposure to UV light to reproduce the effects of solar radiation.
- Corrosion tests in a saline atmosphere to evaluate the resistance of metallic materials.
- Mechanical stresses such as shocks, tension or bending to test structural endurance.
The objective of these tests is to validate the durability of the materials and to identify the degradation mechanisms that may affect their performance.
Why are accelerated aging tests essential for industry?
Industrial companies must ensure that their products withstand real-world conditions. Defective materials or premature degradation can lead to safety risks, product recalls, and significant economic losses .
Accelerated aging tests allow manufacturers to:
- Evaluate the lifespan of products by anticipating their long-term behavior.
- Improve the formulation of materials to enhance their resistance to external aggressions.
- Comply with regulatory requirements by demonstrating product reliability before marketing.
- Optimize development times by reducing the time needed to test the stability and robustness of materials.
For example, in the automotive industry, these tests are used to ensure the longevity of plastics, paints, and electronic components under extreme weather conditions. In the medical sector, they allow for verification of the stability of packaging and sterile medical devices over several years.
Objectives and challenges of accelerated aging tests
The implications of accelerated aging tests are numerous and vary depending on the sector of activity. However, the main objectives remain the same:
- Detecting degradation mechanisms : Understanding how a material reacts to external aggressions (heat, humidity, light, chemicals).
- Predicting the lifespan of a product : Determining how long it takes for a product to lose its properties and become unusable.
- Validate compliance with standards : Ensure that the materials meet the applicable regulatory and safety requirements.
- Optimize product design : Enable manufacturers to improve the robustness and performance of their products before they are put on the market.

Why perform accelerated aging tests?
Accelerated aging tests have become an essential step in many industrial sectors. They allow manufacturers to predict product durability and optimize product design based on the environmental constraints they will be subjected to. The goal is to guarantee the quality, reliability, and safety of materials while meeting regulatory requirements. This section explores the main reasons why manufacturers use these tests and the advantages they provide.
Anticipating the lifespan of products
One of the major concerns for manufacturers is predicting the lifespan of products before they are released to the market. Materials undergo progressive deterioration under the effect of external factors:
- High temperatures accelerate chemical reactions and alter the structure of polymers, coatings, and composites.
- Humidity leads to hydrolysis and the proliferation of microorganisms that can weaken certain materials.
- UV rays cause color degradation, cracking, and mechanical weakening of plastics and paints.
- Mechanical cycles (bending, tension, compression) test the fatigue resistance of structural components.
Thanks to accelerated aging tests, it is possible to compress several years of natural wear into just a few weeks by subjecting products to extreme but controlled conditions. The results obtained allow for an estimation of their actual lifespan and the identification of potential weaknesses.
Ensuring the reliability and safety of materials
In sensitive sectors such as automotive , aerospace, healthcare, and food processing , the robustness of materials is crucial. Premature degradation can lead to serious failures , endangering users and generating significant product recall costs.
Accelerated aging tests verify the ability of materials to maintain their physical, chemical, and mechanical properties over the long term. For example:
- In the automotive industry , plastic parts subjected to high temperatures in the passenger compartment must retain their rigidity and not release toxic substances.
- In the field of medical devices , sterile packaging must remain airtight throughout the product's shelf life.
- In the food industry , packaging must provide effective protection against moisture and oxygen to prevent food spoilage.
These tests also help to avoid risks associated with migration phenomena . Some plastics or coatings can release undesirable chemicals over time, which is particularly concerning for food packaging and medical devices.
Comply with regulatory standards and certification requirements
Accelerated aging tests are often required by industry and regulatory standards to ensure product conformity. Different certifications mandate specific tests depending on the sector of activity:
- ASTM F1980 : Accelerated Aging of Medical Devices and Sterile Packaging.
- ISO 4892 : Aging of plastic materials under UV irradiation.
- ASTM B117 : Salt spray corrosion tests.
- ISO 11607 : Validation of medical packaging.
- EC Regulation 1935/2004 : Control of migration of materials in contact with foodstuffs.
By conducting these laboratory tests, manufacturers ensure that their products meet current requirements and can be safely marketed. This also helps protect them against potential legal challenges related to the durability and safety of materials.
Reduce time to market
In a competitive environment, companies must constantly accelerate product development while ensuring quality. Accelerated aging tests offer considerable time savings compared to real-world studies, which can extend over several years.
By integrating these tests from the design phase, it is possible to quickly identify the highest-performing materials , adjust formulations, and optimize production. This approach allows for faster product launches while minimizing the risk of defects .
Furthermore, these tests are particularly useful in the context of innovation projects . For example, companies developing new coatings, plastics or packaging can compare different formulations in a few weeks and select the best solution.
An indispensable tool for quality and innovation
Accelerated aging tests are not merely a regulatory requirement or an industrial constraint. They represent a genuine opportunity for continuous improvement and innovation . By studying degradation mechanisms, companies can develop stronger, more durable, and more environmentally friendly materials .
In the current context where sustainability and eco-design are major issues, these tests make it possible to meet consumer expectations by offering more robust products with less environmental impact.
Are you looking for an analysis?

The scientific principles of accelerated aging
The chemical and physical reactions of aging
Industrial materials and products inevitably undergo transformations over time under the influence of various environmental stresses. These transformations can be chemical , physical, or mechanical , and their intensity depends on the conditions of exposure.
- Chemical reactions are primarily due to oxidation, photodegradation, hydrolysis, or unintentional polymerization. For example, plastics can become brittle under the effect of UV radiation due to the breakage of polymer chains.
- Physical changes involve alterations in the material's structure, such as swelling, shrinkage, or the migration of certain components. Paints and coatings can lose their adhesion due to variations in temperature and humidity.
- Mechanical alterations are linked to wear, material fatigue, and the formation of microcracks under the effect of repeated stresses.
Laboratories must be able to identify these transformations and determine their impact on product lifespan. This is why accelerated aging tests rely on predictive scientific models to extrapolate results obtained under controlled conditions.
Applying Arrhenius' Law to Accelerated Aging
One of the most widely used models for predicting the aging rate of materials is the Arrhenius equation . This mathematical equation allows us to estimate how temperature influences the rate of chemical reactions that degrade a material. It is formulated as follows:
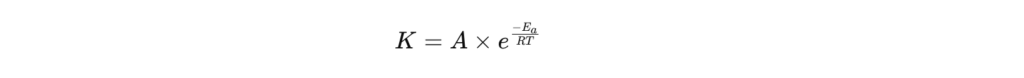
Or :
- K is the aging reaction rate, that is, the speed at which the transformations occur.
- A is a frequency factor specific to the material being studied.
- Eₐ is the activation energy of the degradation reaction.
- R is the ideal gas constant (8.314 J/mol·K).
- T is the temperature in Kelvin.
This law implies that increase in temperature exponentially accelerates the aging of a material . In practice, a 10°C increase often doubles the degradation rate (Q10 factor = 2), although this approximation needs to be validated experimentally for each material.
The use of the Arrhenius equation allows laboratories to define aging equivalencies . For example, a test performed at 50°C for 120 days can be interpreted as 4 years of actual aging at 25°C . This method allows manufacturers to anticipate the long-term behavior of their products without having to wait several years for results.
Factors influencing the aging of materials
The aging of a material depends on many environmental parameters. The main factors taken into account in accelerated testing are:
- Temperature : It accelerates chemical reactions and physical transformations, directly influencing the degradation of polymers, adhesives and coatings.
- Humidity : It promotes the hydrolysis of organic materials, the corrosion of metals and the proliferation of microorganisms that can weaken surfaces.
- UV radiation : It causes photo-degradation of polymers, discoloration of pigments and loss of mechanical resistance of materials exposed to the sun.
- Mechanical stresses : These simulate the fatigue cycles, vibrations and shocks that products undergo during their use.
- Chemical agents : Some materials can be altered by chemical substances present in the air or in their environment of use (pollutants, solvents, cleaning products).
The laboratories design experimental protocols adapted to each product by combining these different parameters in order to best simulate the real conditions of use.
The importance of controlled experimental conditions in the laboratory
To ensure reliable and reproducible results, accelerated aging tests must be carried out under strictly controlled conditions.
- Climate chambers make it possible to maintain a constant temperature and humidity throughout the duration of the tests.
- UV aging chambers are designed to faithfully reproduce solar exposure using specific lamps that emit UV radiation comparable to that of the sun.
- Salt spray tests are used to test the resistance of materials to corrosion by simulating an aggressive marine or industrial environment.
- Mechanical fatigue testing machines apply cycles of compression, bending or tension to evaluate the resistance of materials to repeated stresses.
One of the key aspects of these tests is the standardization of protocols . The methods used must comply with international standards (ASTM, ISO, SAE, CE) to ensure that the results are usable and comparable to other studies.
A scientific tool at the service of industry
Accelerated aging tests are not limited to the empirical observation of the effects of time on a material. They rely on scientific models and rigorous protocols to guarantee results that are usable by industry.
Thanks to advanced analytical tools, laboratories can precisely quantify changes in material properties and identify the degradation mechanisms involved. This data is essential for optimizing product design, ensuring reliability, and meeting regulatory requirements.

The different methods of accelerated aging
Thermal aging: an accelerator of chemical reactions
Increasing the temperature is one of the most effective ways to accelerate the aging processes of materials. By applying a temperature higher than that of normal operating conditions, it is possible to double, triple, or even quadruple the rate of the chemical reactions responsible for degradation.
The most commonly used method is the application of the Arrhenius model , which calculates the equivalence between laboratory aging and actual exposure time at room temperature. For example, a 120-day test at 50°C can simulate 4 years of actual aging at 25°C . This type of test can be performed as part of a qualification process for aging in a climate chamber .
Thermal aging is particularly suitable for:
- Polymers and plastics , in order to assess their dimensional stability, mechanical resistance and resistance to extreme temperatures.
- Paints and coatings , in order to test their adhesion and resistance to cracking under the effect of heat.
- Medical devices , where it is crucial to ensure that materials remain intact and do not release undesirable substances over time.
However, it is essential not to exceed certain critical temperatures , otherwise unrealistic degradation phenomena may occur. Excessive temperature can lead to chemical reactions that would not occur under normal conditions, thus distorting the interpretation of the results.
Aging under controlled humidity and humidity
Humidity plays a major role in the aging of materials, particularly those susceptible to hydrolysis, corrosion, or microbial growth. In this type of test, samples are placed in climate chambers where temperature and relative humidity are carefully controlled.
Controlled humidity tests are primarily used for:
- Testing the resistance of polymers and composites to hygrometric variations , by measuring their swelling or brittleness.
- Evaluate the effect of humidity on the corrosion of metals , particularly in marine or industrial environments.
- Check the stability of pharmaceutical and food packaging to avoid moisture transfers that could alter the packaged products.
Certain materials, such as barrier plastics, must be tested to ensure they retain their insulating properties despite prolonged exposure to a humid environment. These analyses are crucial in the food , packaging , and construction .
UV aging and photoaging: the impact of solar radiation
Materials exposed to natural light undergo progressive degradation under the effect of ultraviolet (UV) rays . Solar radiation is one of the main factors in the aging of plastics, paints, textiles, and composites, leading to alterations such as:
- The discoloration of pigments and coatings.
- The weakening of plastics due to the breaking of polymer chains under the effect of UV radiation.
- The oxidation of materials , which accelerates their degradation and loss of mechanical properties.
UV aging tests are performed in an accelerated photoaging chamber , where UV lamps faithfully reproduce the sunlight spectrum. These tests make it possible to assess the durability of materials in outdoor environments and to predict their behavior after several years of natural exposure.
Some laboratories use standardized protocols , such as ISO 4892 or ASTM G154 , which define UV exposure conditions and simulation cycles. These tests are essential for the building, automotive, and outdoor furniture , where weather resistance is a key quality criterion.
Aging through accelerated oxidation
Some materials, particularly polymers and food products, degrade through oxidation when exposed to atmospheric oxygen. This chemical reaction is amplified by temperature, humidity, and the presence of catalysts such as heavy metals.
To assess this degradation, laboratories use tests under an oxygen-enriched atmosphere . This method makes it possible to simulate oxidation at room temperature without resorting to thermal aging , which makes it more representative of real-world conditions.
It is particularly suitable for:
- Food packaging , where the aim is to limit the oxidation of packaged products.
- Oils and fats , whose stability is essential to guarantee their nutritional and sensory quality.
- Oxidation-sensitive polymers , such as polyurethane or rubber, lose their mechanical properties upon prolonged contact with oxygen.
This approach is an interesting alternative to conventional tests, as it avoids artifacts related to temperature rise , which could skew the results.
Aging under mechanical and chemical stresses
Materials and technical components are often subjected to repeated mechanical stresses during their use. Mechanical aging tests allow us to evaluate their resistance to:
- Cyclical fatigue (tension, compression, flexion).
- Thermal shocks , where samples are subjected to sudden temperature changes.
- Vibrations , particularly for automotive and aeronautical parts.
In parallel, some materials must be tested in the presence of aggressive chemical agents such as solvents, detergents, or acids. These tests are commonly carried out in the context of:
- The cosmetics industry , to verify the stability of containers and formulas exposed to chemical substances.
- Electronics , where printed circuits must withstand cleaning agents and industrial fluids.
- The medical field , where equipment must withstand sterilization cycles without alteration.
Tests combining mechanical, chemical and thermal stresses provide a comprehensive view of product aging and allow for the anticipation of potential failures before they are placed on the market.
A range of methods for diverse needs
Accelerated aging encompasses a variety of techniques adapted to specific materials and conditions of use. Each method is based on precise scientific principles and must be rigorously applied to guarantee reliable results.

Industrial applications of accelerated aging tests
Agri-food sector: ensuring the shelf life of food and packaging
In the agri-food industry , product sustainability is not limited to nutritional and organoleptic quality. It also includes packaging stability and food safety throughout its shelf life.
Prediction of the best before date (BBD)
Long-life food products, such as canned goods, dried goods, or frozen foods, have a best-before date . This date indicates the period during which the product retains its original properties.
Accelerated aging tests allow us to estimate this duration by subjecting food to temperatures higher than those of normal storage conditions. These tests are based on the Arrhenius law and the Q10 factor , which links the rate of degradation to temperature.
These tests allow us to evaluate several parameters:
- The evolution of organoleptic properties (texture, taste, color).
- Nutritional losses (vitamins, antioxidants).
- The appearance of microbiological defects , even on stabilized products.
Thanks to these analyses, manufacturers can adjust product formulations and adapt storage recommendations to guarantee optimal quality.
Food packaging migration tests
Food packaging must provide effective protection against moisture, oxygen, and contaminants. It must also prevent any transfer of undesirable substances into the food.
Accelerated aging tests simulate the interactions between packaging and the product under real and extreme conditions. These tests are particularly useful for:
- Check the stability of packaging materials under the effect of temperature and humidity.
- Evaluate the chemical migration of plasticizers, inks or glues into food.
- Ensure compliance with European and American standards (EC Regulation No. 1935/2004, FDA).
These studies ensure that food packaging preserves the integrity of the food and complies with current health requirements.
YesWeLab supports these projects with its agri-food laboratory analyses.
Stability tests of formulations
Accelerated aging tests allow for the evaluation of the stability of cosmetic products over short periods, as part of a stability test . These tests take place in climate chambers, where the formulas are subjected to:
- Thermal cycles to simulate transport and storage conditions.
- Exposure to UV light to measure the sensitivity of dyes and active ingredients to light.
- Packaging compatibility tests to verify that the containers do not release undesirable substances.
These tests make it possible to identify any defects in the formulas: phase separation, precipitation of components, change in viscosity or alteration of the fragrance.
Aging of cosmetic packaging
Cosmetic product containers must withstand chemical and mechanical damage to guarantee the protection of the formulas. Accelerated aging tests allow for the evaluation of:
- The resistance of plastics and varnishes to solvents present in the formulations.
- The durability of printing and labeling under the effects of humidity and UV light.
- The integrity of the closing systems (pumps, caps, tubes) after several opening and pressure cycles.
These tests are crucial to ensure that the packaging does not compromise product quality and complies with international standards. A laboratory stability test is often recommended as a complement.
Medical and pharmaceutical device sector: ensuring compliance and safety
Medical devices and pharmaceutical packaging must meet strict quality criteria to ensure patient safety. Accelerated aging is an essential step in validating the shelf life of medical products .
Aging tests of medical devices
Medical devices, such as implants, syringes, catheters, and sterile packaging, must retain their physical and chemical properties throughout their lifespan. Accelerated aging tests can be used to verify:
- The stability of the materials used (polymers, silicones, metals).
- The integrity of sterile packaging , which must not lose its airtightness over time.
- Compatibility with sterilization conditions , which can alter certain plastics and glues.
These tests are carried out in accordance with standards such as ASTM F1980 and ISO 11607 , which define the validation requirements for medical packaging.
Aging of pharmaceutical packaging
Pharmaceutical packaging must protect medications from moisture, oxidation, and light. Accelerated aging tests simulate these stresses and evaluate:
- Interactions between the drug and its container (migration of plasticizers, absorption of components).
- The deterioration of protective films and bottles under different climatic conditions.
- The stability of tablets and liquids , in particular their preservation of active ingredients.
These analyses ensure that the medications remain effective and safe until their expiry date.
Materials and polymers sector: testing the durability of infrastructure and coatings
Construction materials, composites, and engineering polymers are subjected to extreme conditions in their daily use. Accelerated aging tests allow for the evaluation of their strength and durability before their integration into infrastructure.
Aging of coatings and paints
Paints and varnishes must withstand harsh weather conditions, UV radiation, and chemicals. Accelerated aging tests allow us to:
- Measure the loss of shine and discoloration after UV exposure.
- Testing the adhesion of coatings subjected to temperature and humidity cycles.
- Evaluate corrosion resistance for industrial and marine paints.
These tests are essential to validate the quality of coatings applied to buildings, equipment and infrastructure.
Durability testing of polymers and composites
Engineering polymers must maintain their mechanical and chemical properties over the long term. Aging tests allow us to test:
- The resistance of plastics to thermal and mechanical shocks.
- The deterioration of composites under environmental stresses (rain, UV, pollution).
- Dimensional stability of parts subjected to hygrometric variations.
These tests are essential for the transport, construction and aerospace , where the durability of materials is a key criterion.

Applicable standards and regulations
Standards for medical and pharmaceutical devices
Medical devices and pharmaceutical packaging are subject to strict requirements to ensure patient safety and the preservation of health products. Accelerated aging tests allow for the evaluation of their durability and guarantee their compliance with applicable regulations.
ASTM F1980: Accelerated aging of medical packaging
ASTM F1980 is one of the main standards for aging tests of sterile medical packaging. It defines the conditions for exposure to high temperatures to simulate the degradation of packaging materials over time.
The tests performed according to this standard allow for the evaluation of:
- The integrity of the welds and closure systems of sterile packaging.
- The interactions between the packaging and its contents , including the migration of substances.
- The resistance of plastic films and barrier materials to moisture and heat.
This standard is essential to ensure that medical devices remain protected and functional until their expiry date.
ISO 11607: Requirements for medical device packaging
ISO 11607 complements ASTM F1980 by specifying the design, validation, and performance requirements for sterile medical packaging . It mandates accelerated aging tests to demonstrate that materials retain their properties throughout their lifespan.
The tests conducted according to this standard include:
- Climate tests , simulating extreme temperature and humidity conditions.
- Mechanical tests to evaluate the resistance of packaging to compression, shocks and vibrations.
- Microbiological analyses , in order to guarantee that sterility is maintained over time.
These tests are mandatory to certify packaging for medical devices and guarantee their safe use.
Standards for materials and polymers
Polymer and composite materials must undergo accelerated aging tests to assess their resistance to environmental conditions. International standards govern these tests to ensure accurate and reproducible results.
ISO 4892: Accelerated aging of plastics under UV
ISO 4892 accelerated photoaging tests of polymers exposed to ultraviolet radiation. It defines the test conditions to simulate the effects of sunlight on plastics and coatings.
These tests allow us to measure:
- The degradation of polymers under the effect of UV and heat.
- The variation in color and the loss of shine of the exposed materials.
- Loss of mechanical properties after several irradiation cycles.
The tests are carried out in a UV chamber with lamps reproducing the solar spectrum, and the results are analyzed to determine the stability of the plastics outdoors.
ASTM G154: Aging of Coatings and Paints
ASTM G154 standard specifies test conditions for coatings, paints, and varnishes subjected to aggressive environments. It mandates cycles alternating exposure to UV radiation, humidity, and condensation to simulate several years of natural aging in just a few weeks.
The main evaluation criteria are:
- Resistance to cracking and chipping.
- Loss of adhesion of coatings on different surfaces.
- The modification of the aesthetic and functional properties of paints.
These tests are widely used in the building, automotive and outdoor furniture .
Standards for food and industrial packaging
Packaging must be tested to ensure that it retains its barrier properties and does not release undesirable substances into the packaged product.
EC Regulation 1935/2004: Safety of materials in contact with food
European Regulation EC 1935/2004 requires food packaging manufacturers to demonstrate that their materials do not contaminate food. Accelerated aging tests can verify that:
- No migration of toxic substances occurs.
- The barrier performance of the packaging remains intact after a long period of storage.
- The mechanical properties of films, cardboards and plastics are not altered by humidity or temperature.
These tests are essential to ensure the conformity of food packaging and to prevent any risk to consumer health.
ASTM B117: Salt spray aging
ASTM B117 covers accelerated corrosion testing , particularly for packaging and metallic materials exposed to aggressive environments. It involves placing samples in a chamber saturated with salt spray to simulate several years of exposure in a humid or marine environment.
This method is used for:
- Assessing the corrosion of metals and alloys.
- Testing the resistance of protective coatings on metal packaging.
- Check the integrity of the welds and closure systems of industrial containers.
It is particularly used in the metal packaging, aerospace and automotive .
Industry-specific standards
Some industries require specific standards to validate the durability of their products.
SAE J2020: Accelerated aging in the automotive industry
The SAE J2020 is used in the automotive industry to test the resistance of plastics, paints and coatings exposed to external conditions.
The tests performed according to this standard allow for the evaluation of:
- The resistance of dashboards and plastic trim to UV rays and heat.
- The durability of paints and varnishes on car bodies.
- The impact of temperature and humidity variations on electronic components.
This standard is essential to guarantee the reliability of vehicles over several years.
YesWeLab: a key partner for accelerated aging testing
A network of specialized laboratories for customized testing
YesWeLab collaborates with over 200 partner laboratories across France and Europe. These laboratories specialize in various disciplines, enabling YesWeLab to offer a wide range of accelerated aging tests tailored to the needs of each industrial sector .
YesWeLab's partner laboratories conduct tests on:
- Polymer and composite materials , by evaluating their resistance to UV, humidity and thermal variations.
- Food and pharmaceutical packaging , with migration and compatibility tests with the contents.
- Medical devices , applying ASTM F1980 and ISO 11607 standards to ensure the stability of materials and sterile packaging.
- Cosmetic and pharmaceutical products , with stability tests to guarantee the long-term effectiveness of the formulas.
- Industrial paints and coatings , subjected to adhesion, corrosion and chemical resistance tests.
Thanks to this network of experts, YesWeLab is able to provide accurate analyses tailored to regulatory and industrial requirements .
A digital platform to simplify the management of analyses
One of YesWeLab's main strengths is its all-in-one digital platform , which allows manufacturers to centralize their analytical needs and optimize the management of their accelerated aging tests.
This platform offers several features:
- Ordering and planning analyses : Companies can choose the tests that are appropriate for their products and plan the tests according to their needs.
- Real-time sample tracking : Each test is tracked from sample submission to results receipt, ensuring total transparency.
- Report reception and analysis : Results are available online, with clear interpretations to aid decision-making.
- Data storage and traceability : All tests carried out are archived to facilitate access to reports and ensure regulatory compliance.
This digital approach allows manufacturers to reduce analysis times, better organize their testing campaigns and improve their data management .
Services that comply with standards and regulations
YesWeLab is committed to providing analyses that comply with the strictest standards , thus guaranteeing the reliability and validity of the results obtained.
The tests carried out by its partner laboratories comply with the requirements of the following standards:
- ISO 17025 , which defines the quality criteria for testing laboratories.
- ASTM F1980 and ISO 11607 , for accelerated aging tests of medical packaging.
- ISO 4892 and ASTM G154 , for tests of resistance to UV and climatic conditions.
- EC Regulation 1935/2004 and FDA , for materials in contact with food.
- ASTM B117 , for salt spray corrosion testing.
Thanks to this regulatory compliance, manufacturers can validate their products before they are placed on the market and guarantee their quality in the long term .
Tailor-made support for manufacturers
YesWeLab goes beyond simply connecting companies with analytical laboratories. The company offers personalized support to help manufacturers design their testing protocols and interpret the results obtained.
This support includes:
- Assistance in defining needs : Selection of the accelerated aging methods best suited to the product's constraints.
- Developing test protocols : Defining experimental conditions according to company standards and objectives.
- Interpretation of results : Detailed analysis of data from tests to optimize product design.
This customized service allows companies to improve efficiency and reduce costs associated with accelerated aging tests .
YesWeLab, a strategic partner for manufacturers
Accelerated aging tests are essential to ensure product durability and compliance, but their implementation can be complex and time-consuming. Thanks to its network of partner laboratories, its innovative digital platform, and its customized support, YesWeLab offers manufacturers a turnkey solution for easily performing these tests .
By leveraging YesWeLab's services, companies benefit from reliable testing, optimized analysis management, and comprehensive regulatory expertise , enabling them to improve the quality of their products and secure their market entry.




